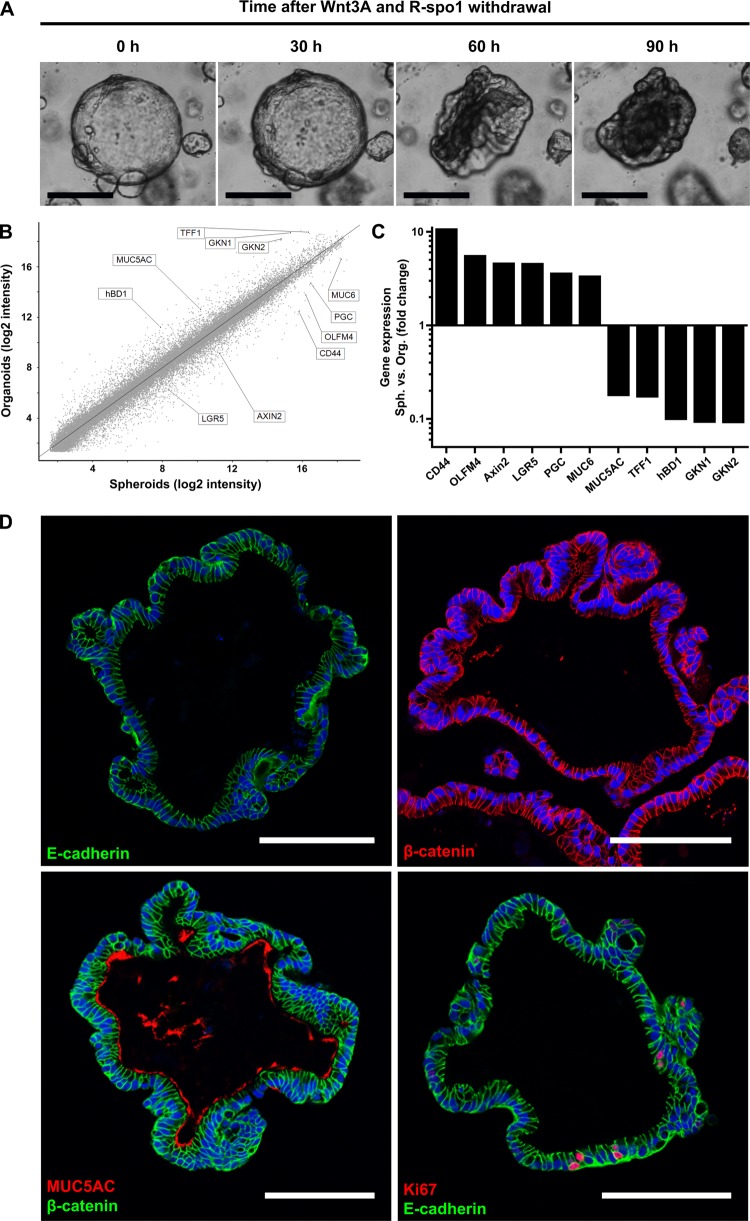
Figure 3.
Human gastric spheroids can be differentiated into organoids. (A) Representative micrographs of different stages of a single spheroid during the differentiation process induced by withdrawal of Wnt3A and R-spondin1. (B) Global overview of differential gene expression upon withdrawal of Wnt3A and R-spondin1 for 5 days as determined by microarray analysis comparing undifferentiated corpus spheroids with differentiated corpus organoids. (C) Expression changes for a selection of gastric-specific and differentiation-specific genes highlighted in the global overview in (B) provided by microarray analysis. For genes with multiple probes, those with the largest difference were chosen. (D) Confocal micrographs of human corpus organoids (cross sections), fluorescently labelled with antibodies against the epithelial marker E-cadherin (green), the polarisation marker β-catenin (red), the pit mucous cell maker MUC5A (red) or the proliferation marker Ki67 (red); nuclei were counterstained with Draq5 (blue). Scale bars: 100 µm.