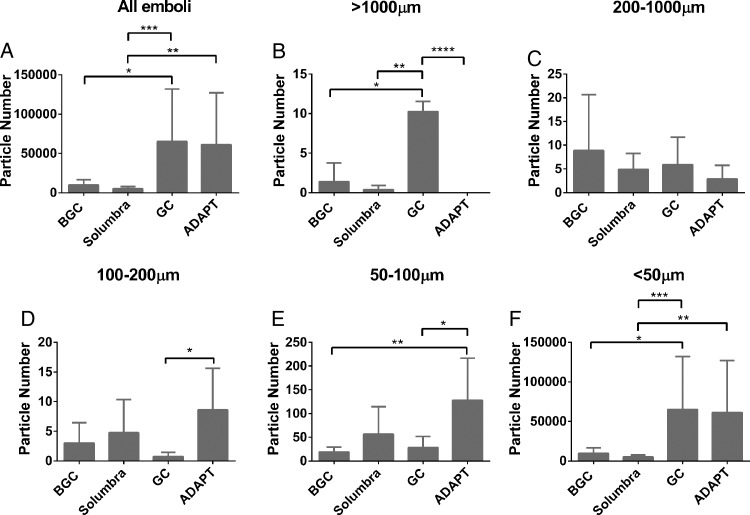
Figure 3.
(A) Total number of hard fragment-prone clot (HFC) emboli. (B, C) Number of HFC clot fragments with size >1000 µm (B) and 200–1000 µm (C). The risk of large clot fragmentation (>1000 µm) is increased with the use of the guide catheter (GC). Average number of HFC fragments with size <200 µm collected during the experiments shown is in D (100–200 µm), E (50–100 µm) and F (<50 µm). The ADAPT technique generates more clot fragments than the other three mechanical thrombectomy techniques (D, E). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001.