Figure 2.
DRN DA Neurons Track Initial Social Contact Following Social Isolation
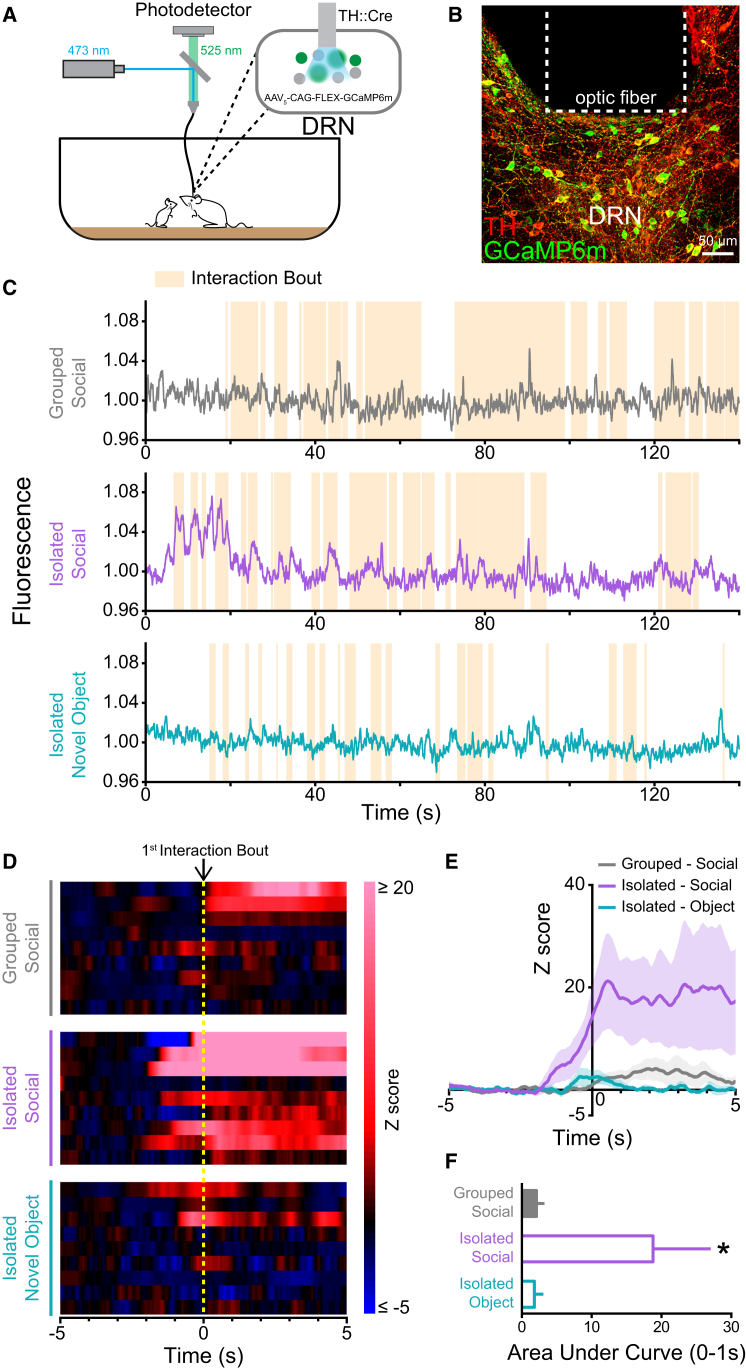
(A) Schematic for recording activity of GCaMP6m-expressing neurons.
(B) Image showing Cre-dependent expression of GCaMP6m in the DRN of a TH::Cre mouse, with optic fiber placement indicated.
(C) Representative traces of bulk fluorescence signal from DRN DA neurons, with shaded areas indicating interaction bouts. Mice were recorded under three conditions: group-housed mice presented with a juvenile mouse (gray), socially isolated mice presented with a juvenile mouse (lilac), or socially isolated mice presented with a novel object (teal).
(D) Heat maps showing the individual Z scores in response to the first interaction bout for each animal under each condition.
(E) Population Z score plots showing the averaged response to the first interaction bout.
(F) DRN DA neurons in socially isolated mice showed a significantly greater increase in activity upon first contact with the juvenile mouse, compared with group-housed mice or response to a novel object (n = 9; one-way ANOVA: F2,16 = 4.978, ∗p = 0.0208; Bonferroni post hoc analysis: ∗p < 0.05 for both comparisons).
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S2 and Movie S1.