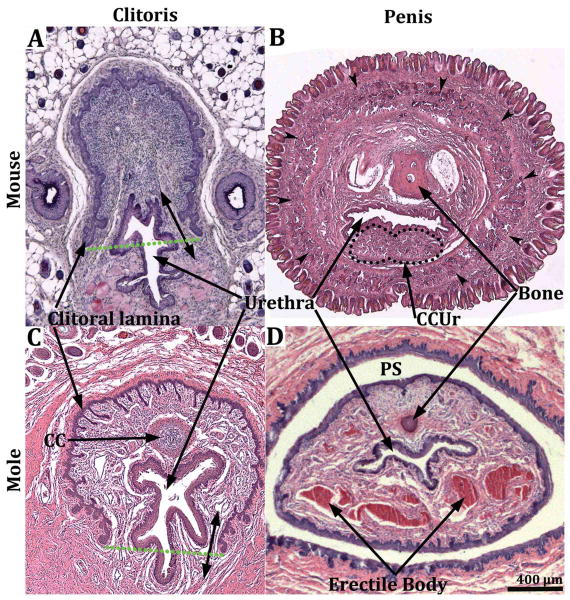
Figure 4.
Transverse sections of the clitoris of the mouse (A) and broad-footed mole (C) and the penis of the mouse (B) and broad-footed mole (D). The clitoris of both species is defined by a U-shaped clitoral epithelial lamina (A & C). The boundaries of clitoral stroma are defined by the clitoral epithelial lamina as well as the green dotted lines. In both species the female urethra is located partially within and partially outside of clitoral stroma. The extent of retention of the urethra within clitoral stroma is dependent upon the proximal/distal position of the section. In more proximal regions the urethra is completely ventral to clitoral stroma, which is the case for both mice and moles. Note the absence of defined erectile bodies within the mouse clitoris (A), and the presence of a corpus cavernosum (CC) located within the clitoral stroma of the broad-footed mole (C). The mouse and broad-footed mole penis is round to oval in shape, contains a urethra, and erectile bodies (double-headed arrows in [B] denote the corpus cavernosum glandis). The corpora cavernosa urethrae (CCUr) is highlighted by a dotted line. Note the network of blood filled cavernous spaces within the penis of the broad-footed mole (D). An os penis is present in both species.