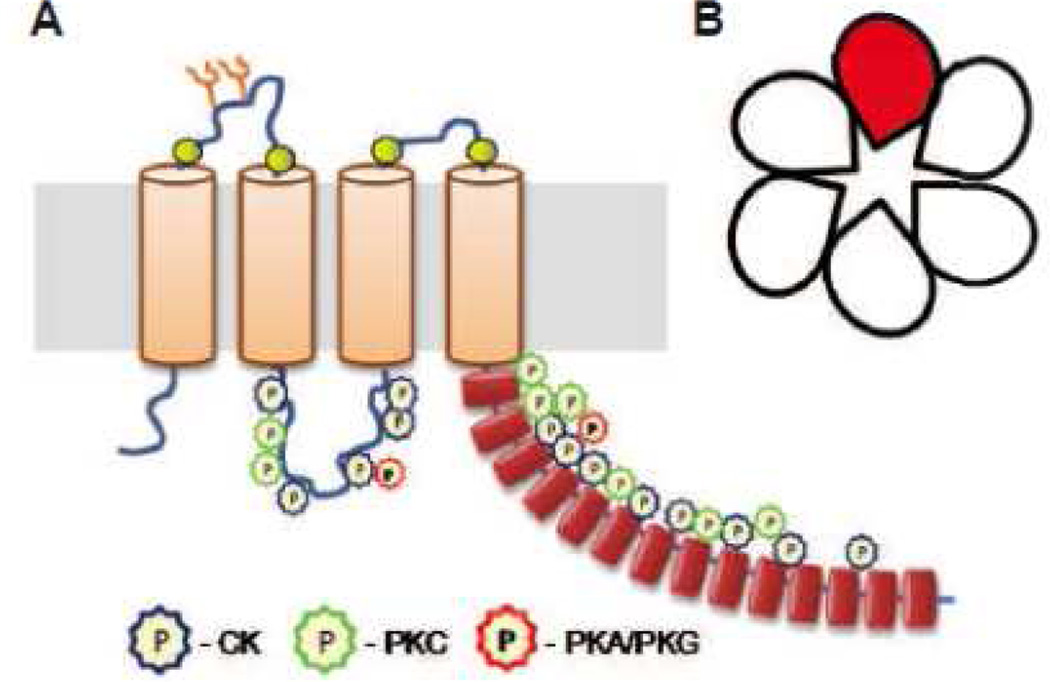
Fig. 4. Schematic representation of the predicted topology of LRRC8A and multimeric composition of the LRRC8 heteromeric complexes forming VRAC.
A, Transmembrane topology of the LRRC8A protein based on the model proposed by Abascal and Zardoya (2012). This diagram contains positions of known glycosylation sites (Y), four conserved cysteines (yellow circles), N-terminal leucine-rich repeat motifs (red cylinders), and putative phosphorylation sites for casein kinase II (CK), protein kinase C (PKC), and cAMP-/cGMP-dependent kinases (PKA/PKG) (color coded multipoint stars, as indicated). The putative phosphorylation sites were determined using LRRC8A sequence from NCBI Protein database (sequence NP_001120717.1) and ScanProsite phosphorylation probability software (Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics. B, Multimeric composition of LRRC8 complexes based on pannexin homology and findings of Voss et al. (2014). Six subunits are proposed to form a channel with one central pore, LRRC8A (red) is an obligatory component of this complex, and has to be heteromerized with at least one of the four other members of the same family (LRRC8B-E) to form a functional VRAC channel. The exact amount of each subunit in heteromer is unknown.