Figure 7. AMPA uncaging currents rectify in BCs but not in MCs .
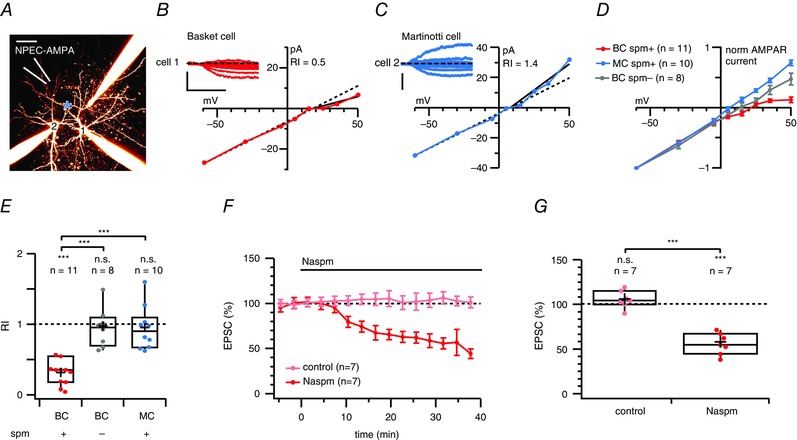
A, 2PLSM maximum intensity projection of a triplet IN recording, with a fourth pipette (white) used for puffing NPEC‐AMPA. Cells were morphologically identified as BC (cell 1) and MC (cell 2) cells. A blue asterisk indicates the location of the 405 nm laser spot. Scale bar = 50 μm. B, submillisecond 405 nm laser pulses elicited AMPAR responses in the BC (cell 1, inset) with slow kinetics (as expected from the NPEC cage) (Palma‐Cerda et al. 2012) that rectified at positive membrane potentials, suggesting the presence of CP‐AMPARs. The RIslope (0.3) was calculated as the I–V slope of peak photolysis‐evoked currents at voltages more positive than the reversal potential divided by the slope at more negative potentials (see Methods). Scale bars = 500 ms, 25 pA. C, for the MC recorded in parallel, however, AMPA uncaging responses did not rectify (cell #2, inset). Scale bars = 150 pA. D, normalized and averaged I–V curves of AMPA uncaging responses recorded in BCs (red) and in MCs (blue) showed that this difference in inward rectification was specific to cell type. In control experiments without internal spermine, BCs did not rectify (grey). E, NPEC‐AMPA photolysis‐evoked responses were rectifying in BCs (red) but not in MCs (blue, P = 0.1), nor in BCs without internal spermine (grey, P = 0.6). In addition, the RI measured in BCs was different from that in MCs and in BCs without internal spermine (Bonferroni corrected), whereas the RIs of MCs and BCs without internal spermine were indistinguishable. The RI in cells recorded from GIN and WT mice was also indistinguishable (0.90 ± 0.1, n = 6 vs. 0.92 ± 0.1, n = 4, P = 0.91). F, ensemble averages show the time course of Naspm blockade of AMPA‐uncaging‐evoked responses (red) compared to stable mock wash‐in controls (light red). G, although mock wash‐in controls were unaffected (P = 0.21), Naspm decreased NPEC‐AMPA photolysis‐evoked responses by half, suggesting the widespread presence of CP‐AMPARs in this cell type.
