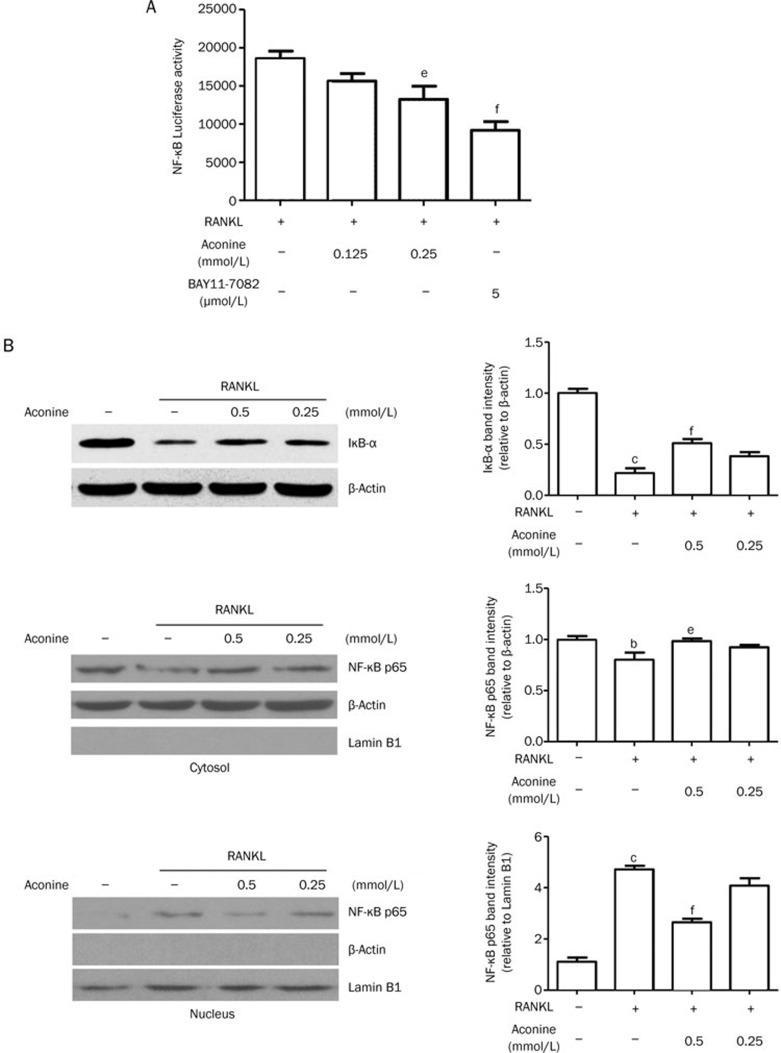
Figure 5.
Aconine inhibits RANKL-induced NF-κB activation. (A) RAW264.7 cells that were stably transfected with a NF-κB luciferase reporter construct were pretreated with varying concentrations of aconine and the NF-κB inhibitor, BAY11-7082, for 30 min and then treated with RANKL (100 ng/mL) for 8 h. (B) RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with aconine for 30 min prior to RANKL (100 ng/mL) stimulation for 30 min. Then, whole cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were extracted as described in the methods. The expression levels of IκB-α, NF-κB p65 in the cytoplasmic and NF-κB p65 in the nuclear extracts were determined using Western blot analysis. Subcellular fraction purity and the equality of sample loading were evaluated by analyzing the levels of β-actin and Lamin B1. Protein levels were quantified using densitometry. Mean±SEM. n=3. bP<0.05, cP<0.01 vs control; eP<0.05, fP<0.01 vs only RANKL-treated cells.