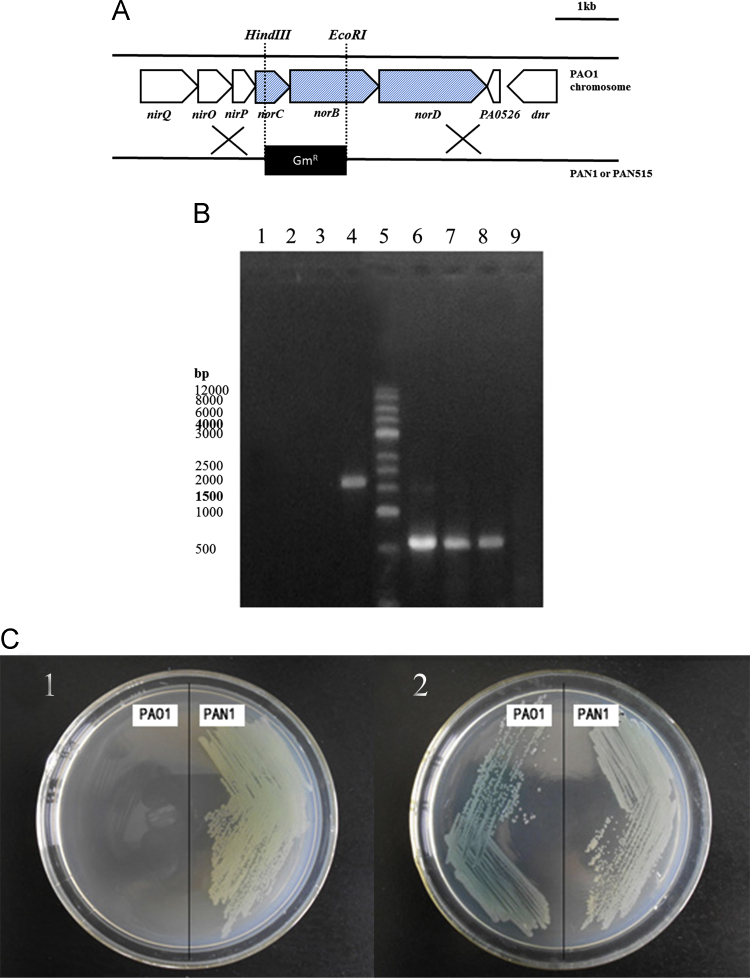
Fig. 3.
PCR and antibiotic resistance test. (A) A construction of the norBC mutant strain of P. aeruginosa. The gentamicin-resistance cassette was inserted into the norBC region by homologous recombination, which resulted in total deletion of norB and partial deletion of norC. The restriction sites used for the construction are shown. GmR, gentamicin resistance. (B) The PCR test: Lane 1: the PCR product of pEXB1lacZ using the NOREF/NORHR primer; Lane 2: the PCR product of PAN1 using the NOREF/NORHR primer; Lane 3: the PCR product of the PAN1 (parallel sample) strain using the NOREF/NORHR primer; Lane 4: the PCR product of PAO1 using the NOREF/NORHR primer; Lane 5: Marker; Lane 6: the PCR product of pEXB1lacZ using the lacZ-F/NORHR primer; Lane 7: the PCR product of PAN1 using the lacZ-F/NORHR primer; Lane 8: the PCR product of PAN1 (parallel sample) using the lacZ-F/NORHR primer; Lane 9: the PCR product of PAO1 using the lacZ-F/NORHR primer; (C) The antibiotic resistance test: (C1) growth of PAO1 and its disruption mutants on PIA medium containing Gm (only PAN1 could grow); and (C2) growth of PAO1 and its disruption mutants on PIA medium (no antibiotic was added, and all of the strains could grow well on it).