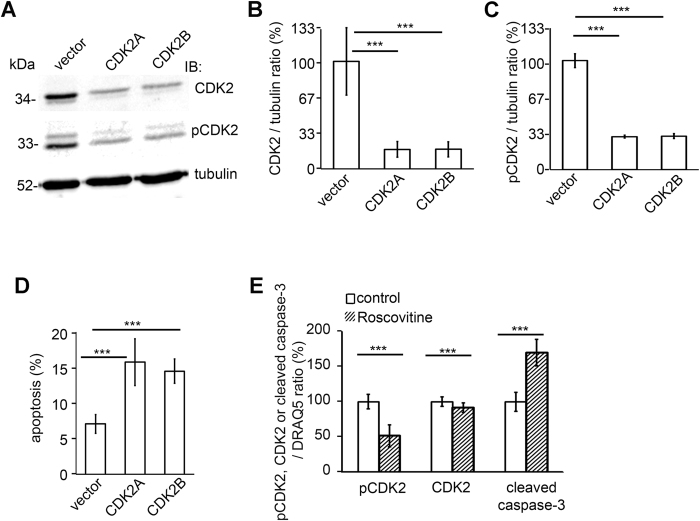
Figure 6. Knockdown of CDK2 by shRNAs increases apoptosis in cultured human podocytes.
(A) Representative immunoblot for CDK2 and phospho-CDK2 (pCDK2, Thr160) in CDK2 knockdown cells. Podocytes were infected using two different shRNA constructs targeting CDK2 (CDK2A, CDK2B). Empty vector (vector) shRNA served as a control. Tubulin is included as a loading control. (B) CDK2 protein level is significantly decreased by both shRNAs compared to empty vector shRNA. (C) Quantification of phospho-CDK2 shows that the phosphorylation level of CDK2 is downregulated after knockdown of CDK2. The experiments (A,B) were performed three times with three replicates in each experiment. (D) Flow cytometry of podocytes stained with annexin V confirms that CDK2 knockdown increases podocyte apoptosis. The experiment was performed three times with three replicates in each experiment. Data are presented as mean ± SD. ***p < 0.001 vs. vector group. (E) Quantification of In-Cell Western of phospho-CDK2, CDK2 and cleaved caspase-3 in podocytes treated or not with 25 μM roscovitine shows that the expression of phosphorylated CDK2 and CDK2 are decreased and the expression of cleaved caspase-3 is higher after treatment with roscovitine compared to control. DRAQ5TM was used for normalization. The experiment was performed three times, with 24 replicates per group. Data are presented as mean ± SD, ***p < 0.001 vs. control group.