Figure 4.
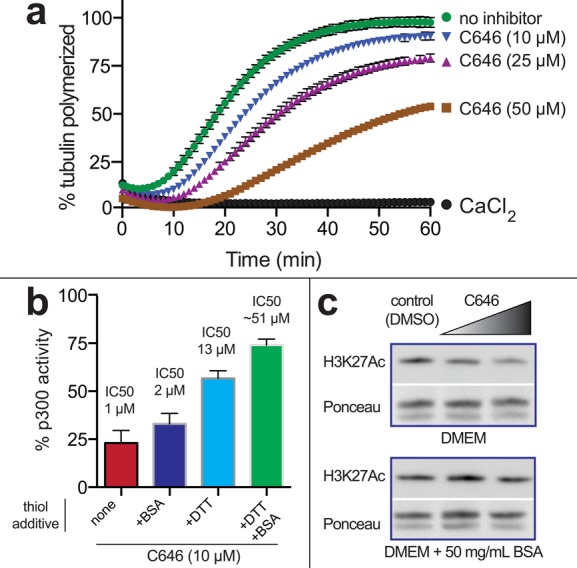
Biological consequences of C646 reactivity. (a) C646 can inhibit tubulin polymerization. Tubulin polymerization was monitored using a fluorescence assay. CaCl2 is a positive control that effectively inhibits tubulin polymerization. (b) In vitro inhibition of p300 by C646 is sensitive to metabolite and protein thiol-containing additives. Full dose–response curves are provided in Figure S4. (c) Cell-based inhibition of histone acetylation by C646 is sensitive to the presence of nucleophiles in cell growth media. Lane 1 (left), vehicle DMSO; lane 2 (middle), 20 μM C646; lane 3 (right), 40 μM C646.
