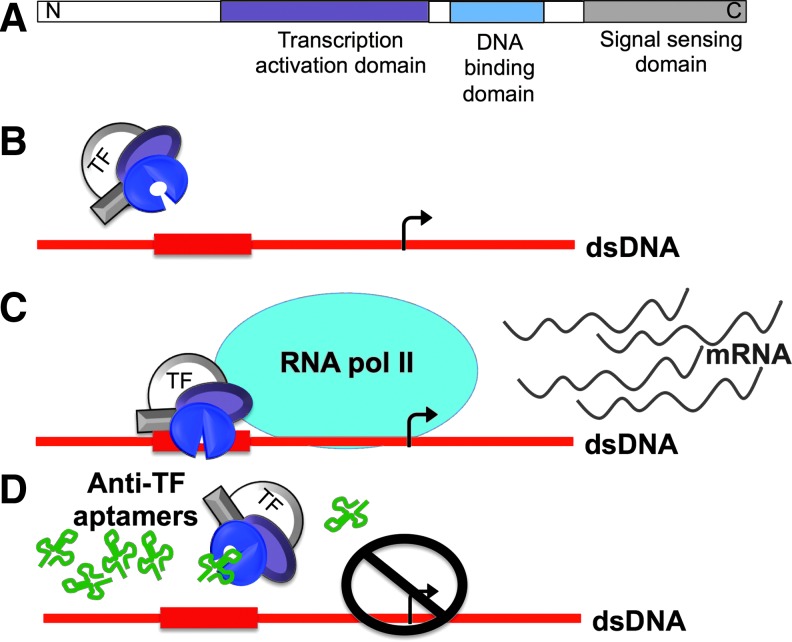
FIG. 1.
Example of transcription factor (TF) modular structure and proposed mechanism of anti-TF aptamers. (A) Schematic illustration of an example TF showing separate structural modules with different functions: transcription activation domain, DNA-binding domain, and signal-sensing domain. (B) Potential mechanism of anti-TF aptamers. TFs are activated and bind to promoter and enhancer consensus sequences. (C) Upon DNA binding TFs promote and regulate chromatin modification and recruitment of RNA polymerase. (D) Aptamers with high specificity and affinity against a TF might competitively bind the target and inhibit binding of TF to dsDNA, resulting in inhibition of gene expression.