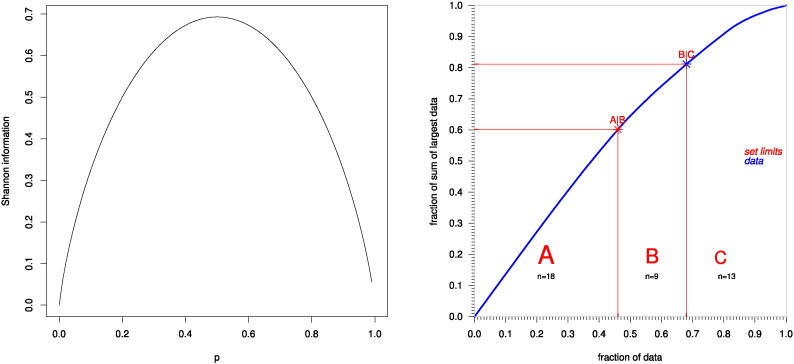
Fig. 1.
Graph of the Shannon information and ABC analysis of the information content provided by the observed number of patients with lesions, relative to all observations, in a particular brain region. Left: Graph of the Shannon information (Shannon, 1951) depicting its formula as Info(BRi) = - p0 , i ∙ ln (p0 , i) - p1 , i ∙ ln (p1 , i) , where p0,i and p1,i are the observed probabilities of the non-observation or observation, respectively, of a brain lesion. Right: ABC plot of the cumulative distribution function of the Shannon information per brain region (blue line).The limits of sets A, B and C resulting from the present ABC analysis are drawn as red lines. For further details about an ABC analysis, see Ultsch and Lötsch (2015). The 13 brain regions assigned to ABC set “C” (Shannon information < 0.32, see Table 1) were not further analyzed because of providing low information judged by the ABC analysis as “trivial”. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)