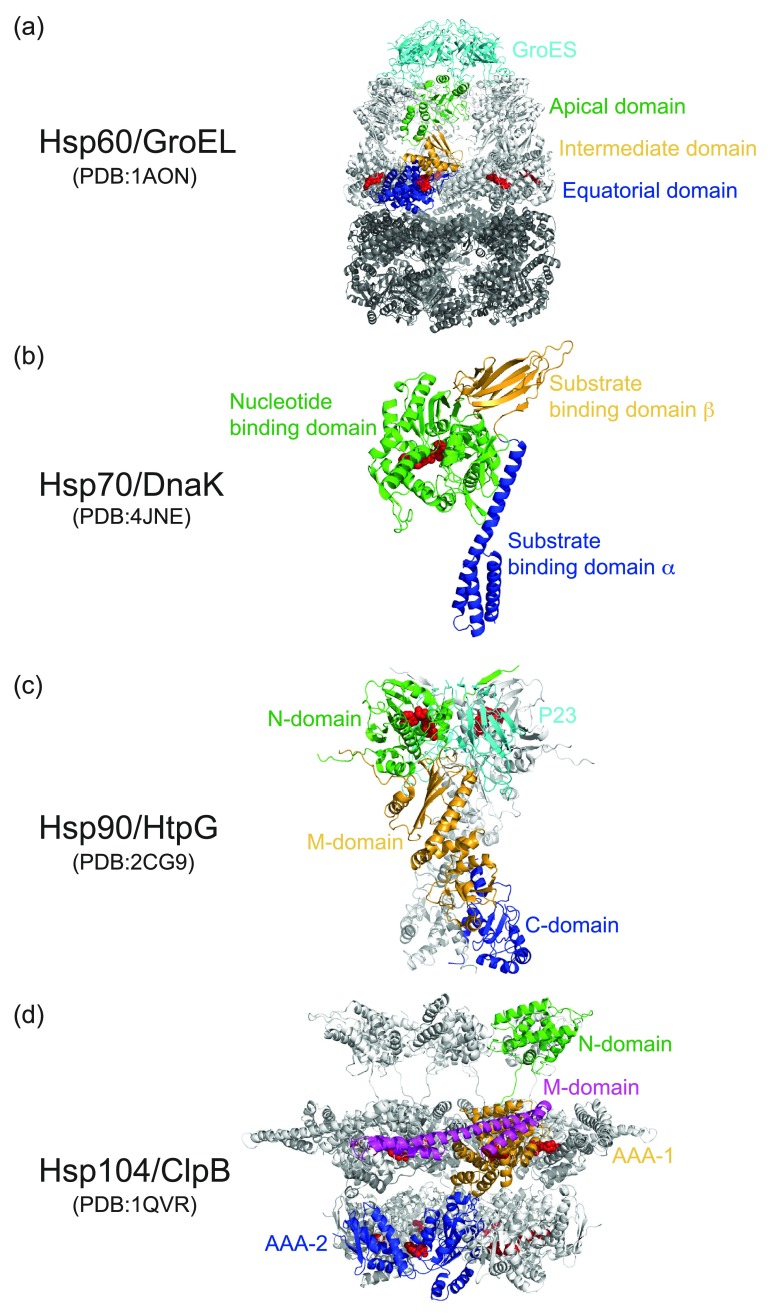
Figure 1. Molecular architecture and domain organization of ATP-dependent molecular chaperones.
Protein is shown as ribbon diagram with the bound nucleotide as red CPK model. For each chaperone, the domains of one subunit are shown in different colors in order of green, orange, and blue from N- to C-termini. Bound co-chaperones are colored cyan. ( a) Hsp60/GroEL: Architecture and domain organization of the E. coli GroEL tetradecamer bound to ADP with a GroES heptamer capping the GroEL cis ring (PDB: 1AON) 33. ( b) Hsp70/DnaK: Architecture and domain organization of the E. coli DnaK monomer in the ATP-bound state (PDB: 4JNE) 54. ( c) Hsp90/HtpG: Architecture and domain organization of the ATP-bound yeast Hsp90 dimer in the closed-state conformation, and its stabilization by p23/Sba1 (PDB: 2CG9) 81. ( d) Hsp104/ClpB: Architecture and domain organization of a yeast Hsp104 hexamer bound to ATP (PDB: 1QVR; EMD-1631) 97, 99. The Hsp104 M-domain that mediates the species-specific interaction with Hsp70 is colored in magenta.