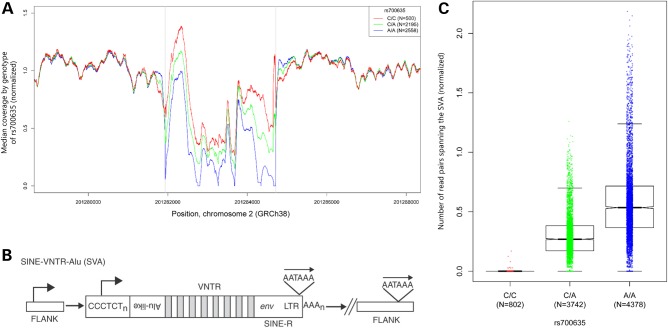
Figure 2.
rs700635[C] is associated with insertion of an SVA-E retrotransposon into the CASP8 gene. (A) The DNA sequence coverage of the CASP8 intron 8 region was normalized and the median coverage for each genotype was plotted at each position. A copy number variation was detected in the region chr2:201281936-201284718 (GRCh38/hg38). Linear regression of mean normalized coverage by SNP genotype showed a significantly higher copy number over this region in association with rs700635[C] (P << 2 × 10−16). (B) The general structure of an SVA element: these non-autonomous retrotransposons consist of a CCCTCT repeat region (which may have RNApolII promoter activity), followed by a series of Alu-like repeats, followed by a VNTR region, followed by a degenerate env gene fragment and long terminal repeat from an extinct endogenous human retrovirus (HERV-K). Transcription in the SVA may utilize a polyadenylation signal within the long terminal repeat, or it may continue into flanking chromosomal sequences (see text). [Image from (17), used with permission.] (C) Boxplot showing association of DNA-sequence read pairs spanning the SVA insertion site with rs700635 genotype: read pairs were selected such that the forward read was in CASP8 sequence within an interval of 1000 bp to the left of the SVA-E insertion site and the paired reverse read was in CASP8 sequence within an interval of 1000 bp to the right of the SVA-E insertion site. Such reads are expected to occur only if the SVA-E retrotransposon is absent. Counts of qualifying reads were normalized and plotted by genotype. Association was assessed by linear regression of read count versus rs700635 genotype (P << 2 × 10−16).