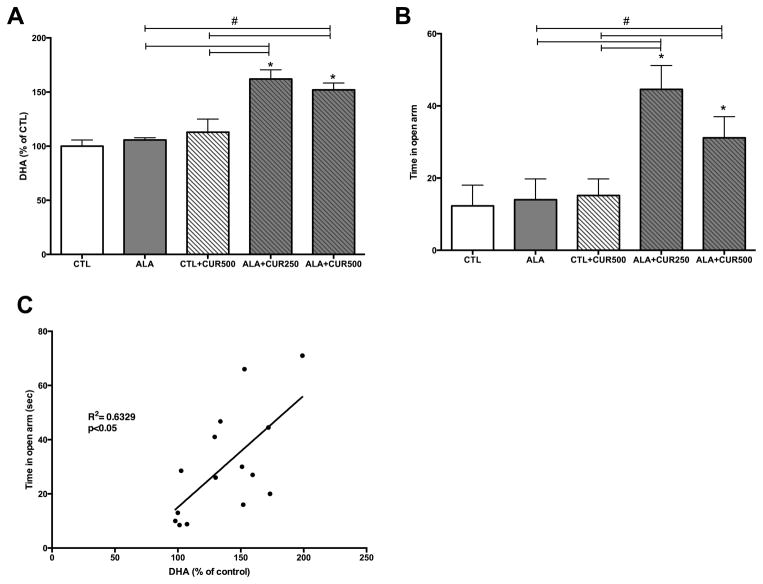
Figure 1. Curcumin combined with ALA increases DHA in the brain, which correlates with reduced anxiety-like behavior.
ALA alone and CUR alone did not increase DHA in the hippocampus (A). A1LA plus CUR significantly increased DHA levels at both 250 and 500 ppm doses of CUR. The time in open arm was significantly higher in ALA+CUR groups compared with CTL or ALA alone (B). DHA in the brain was positively correlated with time spent in the open arm (C). CTL: control, ALA: α-linolenic acid, CUR: curcumin. *compared with control (p<0.05); # compared with indicated p<0.05 (n=5–6)