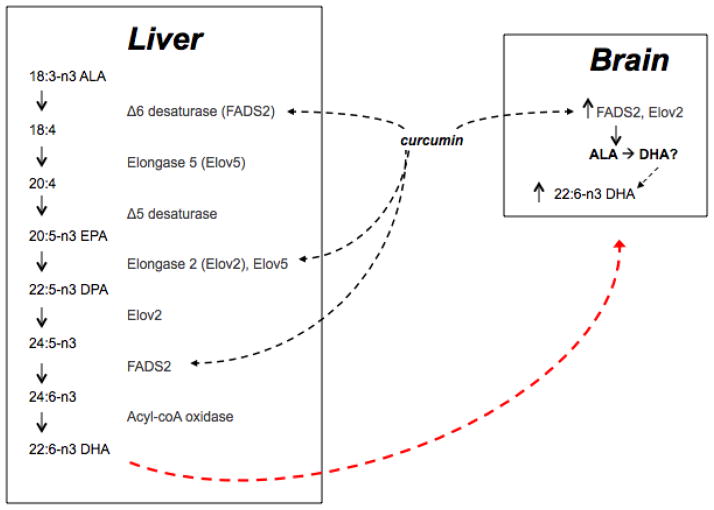
Figure 8. Schematic of the mammalian DHA synthesis pathway and the influence of curcumin.
Curcumin elevates the enzymes FASD2 and Elov2 in both liver and brain tissues and increases DHA levels in these tissues when fed in combination with ALA. In cultured liver cells, curcumin + DPA increases DHA production, an action which is prevented by inhibiting the FASD2 enzyme. Thus we propose that curcumin enhances DHA synthesis by increasing levels of DHA processing enzymes in the liver and brain, though we cannot say for sure whether the increased DHA content in the brain is a product of elevated DHA synthesis in the brain tissue or whether DHA produced in the liver is transported to the brain. FADS2: delta 6 desaturase, Elov2: elongase, ALA: α-linolenic acid DPA: Docosapentaenoic acid, DHA: Docosahexaenoic acid.