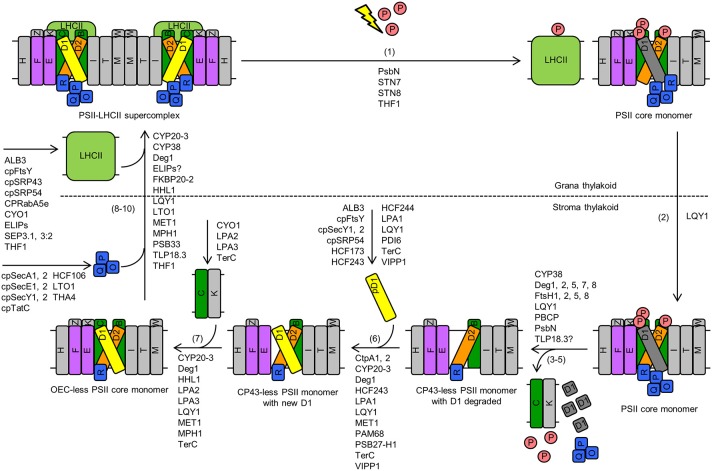
Figure 2.
Damage, repair, and reassembly of PSII in Arabidopsis. The major steps include: (1) high-light-induced phosphorylation, damage, and disassembly of the PSII-LHCII supercomplex and the PSII core dimer in grana stacks, (2) lateral migration of the PSII core monomer to stroma-exposed thylakoid membranes, (3–5) dephosphorylation, partial disassembly of the PSII core monomer, and degradation of photodamaged D1, (6) synthesis and reassembly of new D1, (7) re-incorporation of CP43, (8) reattachment of OEC, (9) migration of the PSII core monomer back to grana stacks, and (10) dimerization into PSII core dimers and reformation of PSII-LHCII supercomplexes. Proteins that are involved in these steps are listed. Although PPL1 might be involved in PSII repair, it is not depicted in this figure because it is not clear which step(s) of PSII repair this protein is involved in. Letters (B, C, D1, D2, E, F, H, I, K, M, O, P, Q, R, T, W, Z) in rectangles represent PSII proteins PsbB (i.e., CP47), PsbC (i.e., CP43), D1, D2, PsbE, PsbF, PsbH, PsbI, PsbK, PsbM, PsbO, PsbP, PsbQ, PsbR, PsbT, PsbW, and PsbZ, respectively. The letter P in a circle represents phosphate. The yellow lightning bolt represents light. Abbreviations: LHCII, light-harvesting complex II; OEC, oxygen-evolving complex; pD1, precursor D1; PSII, Photosystem II. For simplicity, only one name is shown for proteins with multiple names (e.g., “THF1” for THF1/PSB29).