Figure 2.
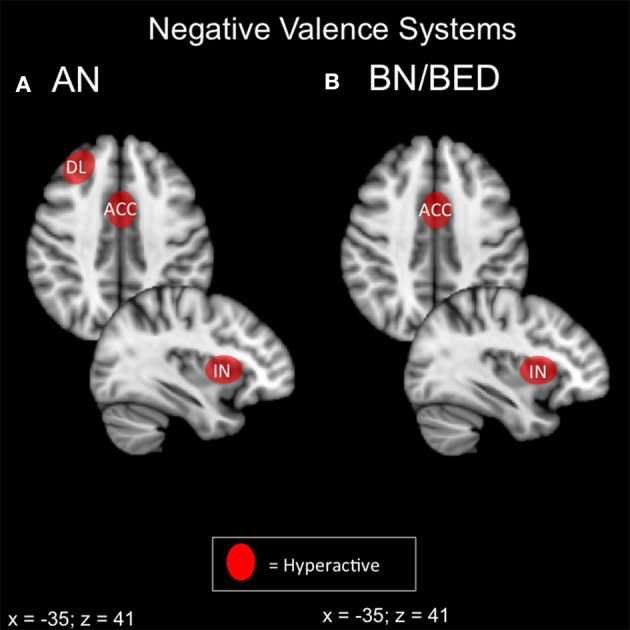
Candidate NIBS targets that address abnormal phenotypes related to the RDoC negative valence dimension. (A) Candidate negative valence NIBS targets for anorexia nervosa (AN) (Ellison et al., 1998; Frank et al., 2002, 2012b; Seeger et al., 2002; Uher et al., 2004; Friederich et al., 2010; Vocks et al., 2010; Cowdrey et al., 2011; Bischoff-Grethe et al., 2013; Strigo et al., 2013; Bär et al., 2015). The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DL) is abnormally hyperactive for pain anticipation and the receipt of punishment. The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) is hyperactive for aversive food stimuli, the receipt of punishment, and anxiety. Finally, the anterior insula (IN) is abnormally hyperactive during anxiety and the anticipation of pain. (B) Candidate negative valence NIBS targets for bulimia nervosa (BN) and binge eating disorder (BED). The ACC is abnormally activated for negative words about the body (Miyake et al., 2010), while the insula is hyperactive during negative affect (Bohon and Stice, 2012).
