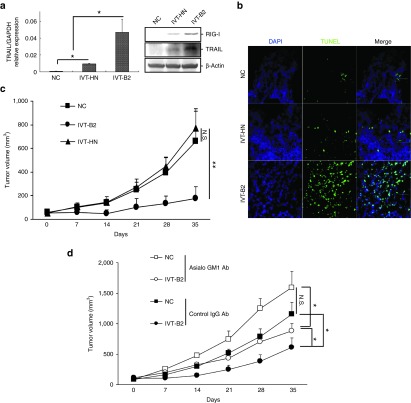
Figure 6.
Transfection of IVT-B2 RNA by in vivo electroporation suppressed PC3 xenograft tumor and induced intratumoral apoptosis in immunodeficient mice. A total of 5 μg of IVT-B2, IVT-HN RNA, or ddH2O only (NC) was transfected into PC3 xenograft tumors by in vivo electroporation in CB-17/SCID mice. (a) The expression levels of RIG-I and TRAIL were evaluated by western blot analysis (right panel), and the transcription of TRAIL was evaluated by real-time quantitative PCR in PC3 xenograft tumors 48 hours after IVT-RNAs transfection (left panel). IVT-B2 (n = 3), IVT-HN (n = 3), and NC groups (n = 3). (b) The apoptotic cells in the PC3 xenograft tumors were evaluated by TUNEL staining 48 hours after transfection with the IVT RNAs. Bar = 100 μm. (c) PC3 xenograft tumor volumes were evaluated. The IVT-RNAs were transfected on days 0, 3, and 6 by in vivo electroporation in the IVT-B2 (n = 7), IVT-HN (n = 8), and NC groups (n = 7). **P < 0.01. (d) IVT-RNAs or ddH2O only (NC) were transfected to PC3 xenograft tumor by in vivo electroporation in CB-17/SCID mice, which were treated with NK cell-depletion using anti-asialo GM1 antibodies or control IgG antibodies. Tumor volumes are shown (mean ± SD) for the IVT-B2 (n = 4), IVT-HN (n = 4), and NC group (n = 3). N.S., no significant difference. *P < 0.05.