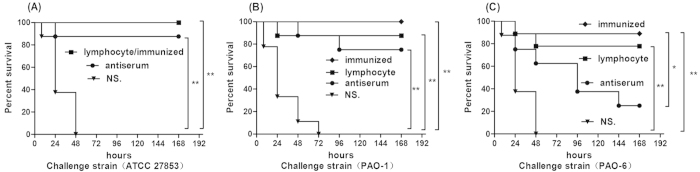
Figure 2. Evaluation of the vaccine induced protection against P. aeruginosa pneumonia in vivo.
Immunized C57BL/6 mice received escalating doses of 108, 5 × 108, 109, and 5 × 109 CFUs irradiated ATCC27853 cells intra-nasally every week. 1 × 107 spleen lymphocytes or 300 μl serum were isolated from the immunized mice and transferred to normal mice 12 h before and after challenge, while controls received normal saline. Kaplan–Meier curves were plotted for mice of the above groups which were challenged by 5 × 106 CFUs the parental strain ATCC 27853 (A), 5 × 106 CFUs homologous serotype PAO-1(B) and 1 × 107 CFUs heterologous serotype PAO-6 (C), and monitored the seven days survival rates. Irradiated vaccine protected mice against intranasal challenge by virulent P. aeruginosa, serum transferred mice showed powerful anti-infectious effect against homologous strain (ATCC 27853 and PAO-1) while T lymphocytes adopter mice survived longer when challenged by the homologous and heterologous serotype strains (ATCC 27853, PAO-1, and PAO-6) than the controls. Results represent three independent experiments (n = 10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).