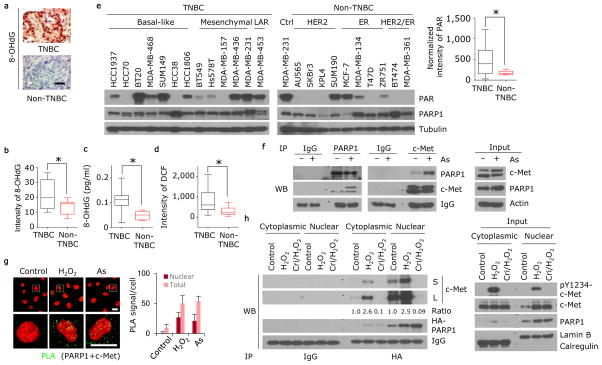
Figure 1. ROS induces the association of c-Met and PARP1.
(a) Human breast cancer tissue microarray was stained with 8-OHdG-specific antibody. Representative images of 216 non-TNBC and 90 TNBC cases are shown. Bar, 100 μm. (b) Human breast cancer cell lines shown in panel (e) were stained with 8-OHdG-specific antibody (see Supplementary Fig. 1a). Quantitation of 8-OHdG is shown. (c) Human breast cancer cell lines shown in panel (e) were subjected to ELISA assay to measure 8-OHdG abundance. (d) Human breast cancer cell lines shown in panel (e) were incubated with 10 μM of DCF-DA for 30 min. Quantitation of DCF is shown. (e) Western blot showing expression of PAR, PARP1, and tubulin in lysates of the indicated human breast cancer cell lines. Blots are representative of triplicate experiments. Right, band intensity of PAR normalized to tubulin. (f) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with or without 20 μM sodium arsenite for 18 h. Left, endogenous PARP1 and c-Met association detected by immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blot. Right, input control. (g) Detection of PARP1 and c-Met co-localization (green signals) in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with H2O2 or sodium arsenite (As), and in those cells not treated (control) by a Duolink assay. Bar, 20μm. Representative images and quantitation of PLA signals from 50 cells and three independent experiments are shown. (h) MDA-MB-231 cells with ectopic expression of HA-tagged PARP1 were treated with 20 μM H2O2 for 30 min with or without a one-hour pre-treatment with 2 μM c-Met inhibitor crizotinib. Left, IP and Western blot analysis of cytosolic and nuclear fractions with the indicated antibodies. The treatment-to-control ratio of c-Met/PARP1 interaction is shown below. Right, input control. TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer. LAR, luminal androgen receptor; As, sodium arsenite; L, long exposure; S, short exposure. Error bars represent s.d. *P < 0.05, t-test.