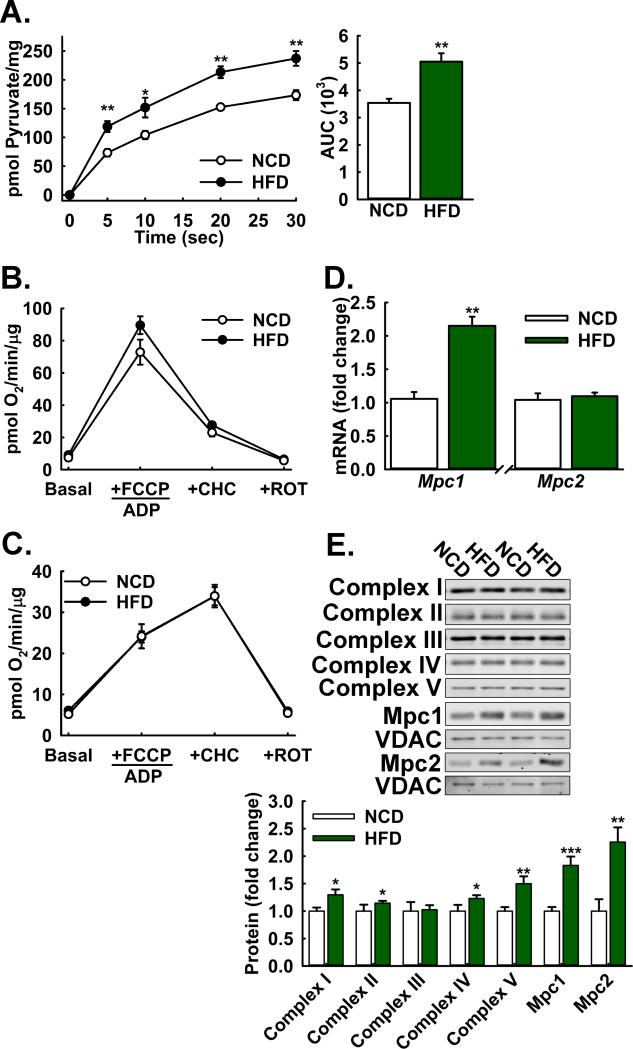
Figure 6. Diet-induced obesity increases hepatic MPC protein levels and Activity.
A: 14C-Pyruvate uptake by liver mitochondria isolated from high fat-diet fed versus age-matched normal chow fed control mice. (n=8)
B,C: (B) Pyruvate-driven (10 mM pyruvate/2 mM malate) and (C) glutamate-driven (10 mM glutamate/2 mM malate) respiration by liver mitochondria isolated from high fat-diet fed versus age-matched normal chow-fed control mice (n=8).
D: Relative Mpc1 and Mpc2 transcript abundance in livers of high fat-diet fed versus age-matched normal chow-fed control mice, normalized to U36b4. (n=8)
E: Western blot analysis of electron transport chain (ETC) components (Complex I-V), and Mpc1, Mpc2, VDAC, and HSP90 proteins in liver lysates from high fat-diet fed versus age-matched normal chow-fed control mice. Densitometric quantification is relative to HSP90. (n=8)
All mice were on a high-fat diet for 22 weeks from 6 weeks of age. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). Also see Figure S6.