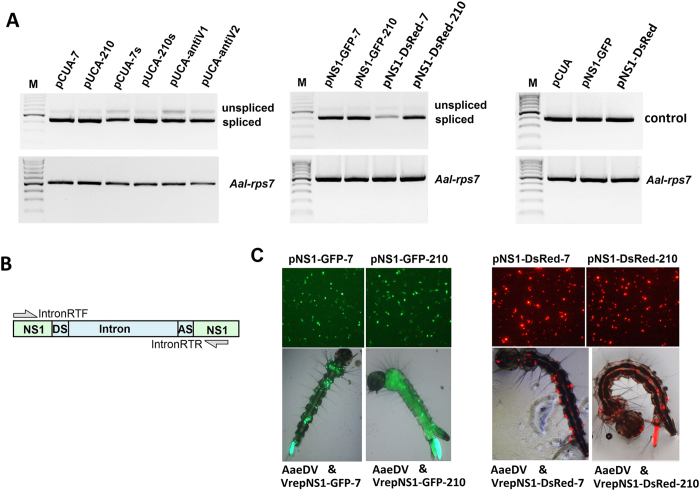
Figure 3. Splicing analysis of the intronic miRNA expression constructs in mosquito.
(A) The horizontal arrows indicate the positions of the primers used for the expression splicing analysis of the intronic miRNA expression constructs. Amplification with IntronRTF and IntronRTR revealed a 407-bp major band that corresponded to ligation of the NS1 exon, whereas the 540-bp faint band corresponded to the non-spliced transcript. Amplification of rpS7 was used as a loading control. Visible bands were gel purified and sequenced. (B) Plasmids pNS1-GFP-7, pNS1-GFP-210, pNS1-DsRed-7 and pNS1-DsRed-7 transfected into C6/36 cells are shown in the top panel. Recombinant virus VrepNS1-GFP-7, VrepNS1-GFP-210, VrepNS1-DsRed-7 and VrepNS1-DsRed-7 transduced larvae are shown in the bottom panel. If the artificial intron is not removed, the frame-shift mutation in the fused fluorescence reporter will preclude the fluorescence. We detected fluorescence in all of the vector-transfected cells and in the recombinant virus-transduced larvae, confirming that the artificial intron functioned in the mosquito cells.