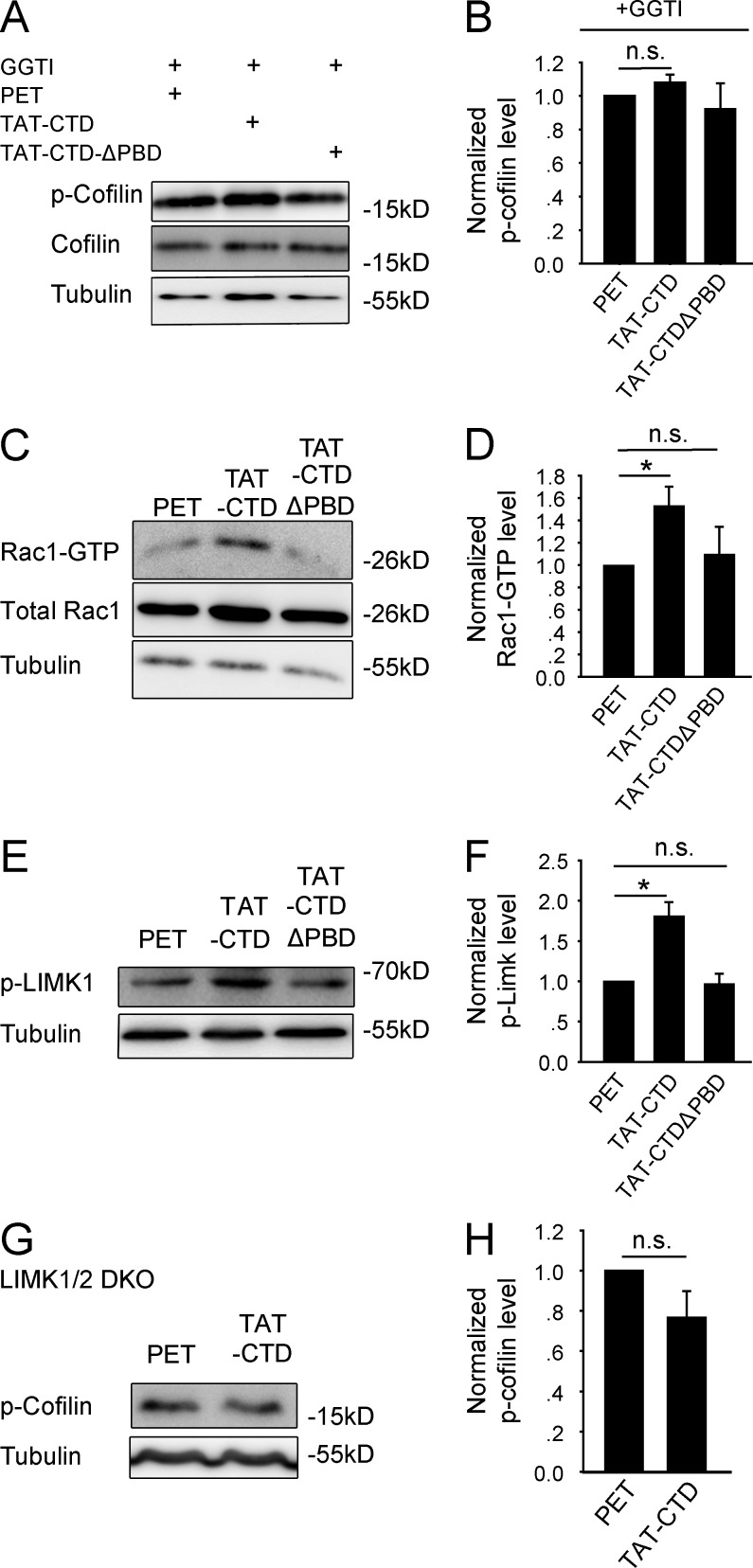
Figure 6.
NLG1 CTD induces cofilin phosphorylation via Rap1/LIMK1 pathway. (A) Western blots of protein lysate of cultured neurons treated with GGTI and various recombinant proteins. (B) Summary graph of A showing similar p-cofilin in TAT-CTD–, TAT-CTDΔPBD–, and PET-treated neurons. (C) Western blots of GTP-bound Rac1 of protein lysate of cultured neurons treated with various recombinant proteins. (D) Summary graph of C showing significantly elevated GTP-Rac1 in neurons treated with TAT-CTD compared with those treated with TAT-CTDΔPBD or PET. (E) Western blots of p-LIMK1 using protein lysate of cultured cortical neurons treated with various recombinant proteins. (F) Summary graph of E showing significantly increased p-LIMK1 in TAT-CTD compared with TAT-CTDΔPBD– or PET-treated neurons. *, P < 0.05. (G) Western blots of protein lysate of LIMK1/2 double-KO brain slices treated with TAT-CTD or PET recombinant proteins. (H) Summary graph of G showing similar p-cofilin in TAT-CTD– and PET-treated LIMK1/2 double-KO brain slices. n.s., not significant.