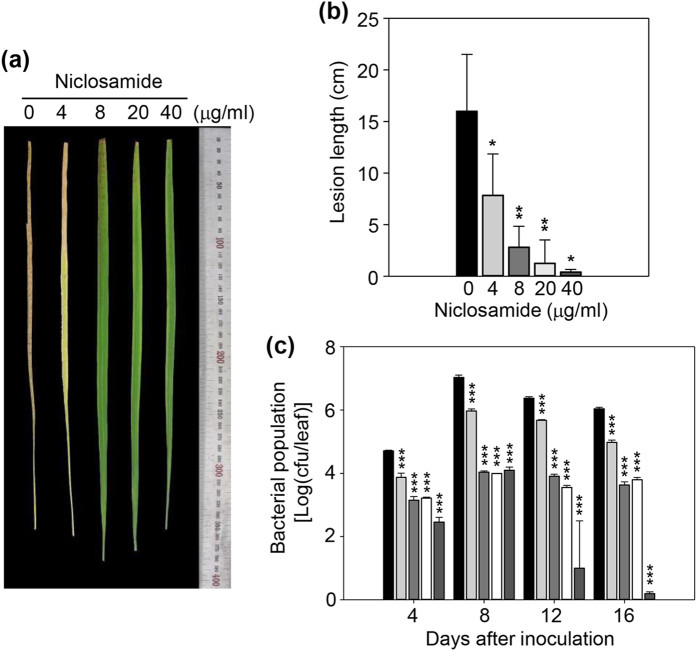
Figure 2. Niclosamide dosage effects on rice disease responses to the representative Xoo strain PXO99.
(a) Leaves were inoculated with PXO99 bacterial suspension using the leaf-clipping method and the plants sprayed with different niclosamide concentrations. Photographs were taken at 16 days post-inoculation. (b) Lesion development was examined by measuring lesion length in PXO99-treated plant leaves or niclosamide- and PXO99-treated plant leaves. Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in lesion lengths (*p < 0.01; **p < 0.001; Student’s t-test) between untreated and niclosamide-treated leaves. (c) Leaves of PXO99-treated plants or niclosamide- and PXO99-treated plants were sampled at the indicated time points. The samples were ground, suspended in sterile water, and plated onto peptone-sucrose agar medium containing cephalexin. The numbers of bacterial colonies were then counted. Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars.  , PXO99 only;
, PXO99 only;  , PXO99 plus 4 μg/ml niclosamide;
, PXO99 plus 4 μg/ml niclosamide;  , PXO99 plus 8 μg/ml niclosamide; □, PXO99 plus 20 μg/ml niclosamide;
, PXO99 plus 8 μg/ml niclosamide; □, PXO99 plus 20 μg/ml niclosamide;  , PXO99 plus 40 μg/ml niclosamide. Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in bacterial populations (***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test) between untreated and niclosamide-treated leaves at different time points after PXO99 inoculation.
, PXO99 plus 40 μg/ml niclosamide. Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in bacterial populations (***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test) between untreated and niclosamide-treated leaves at different time points after PXO99 inoculation.