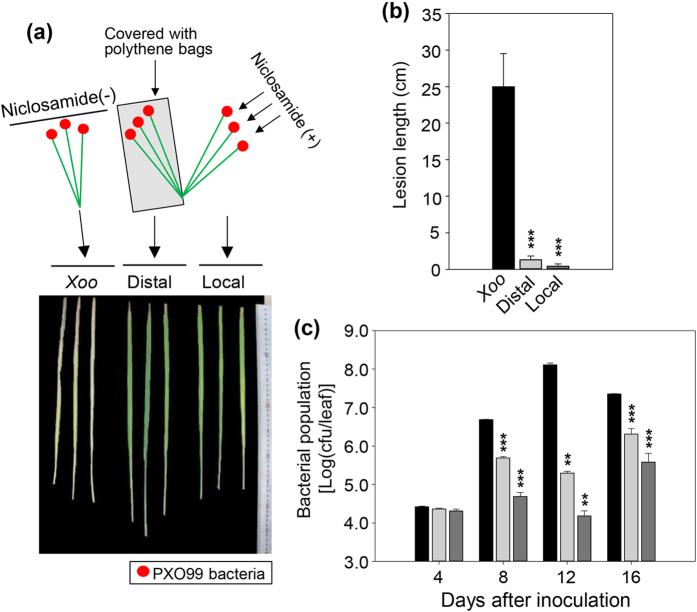
Figure 4. Systemic effects of niclosamide on rice disease responses to the representative Xoo strain PXO99.
(a) Leaves were inoculated with PXO99 bacterial suspension using the leaf-clipping method (left panel). Half of the leaves were covered with polythene bags (middle panel) and the remaining leaves were sprayed with niclosamide (right panel). Photographs were taken at 16 days post-inoculation. (b) Lesion development was examined by measuring lesion length in PXO99-treated plant leaves or the local and distal leaves of niclosamide- and PXO99-treated plant leaves. Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in lesion lengths (***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test) between untreated and niclosamide-treated local leaves or between untreated and niclosamide-treated systemic leaves. (c) Leaves of PXO99-treated plants or local and distal leaves of niclosamide- and PXO99-treated plants were sampled at the indicated time points. Samples were ground, suspended in sterile water, and plated onto peptone-sucrose agar medium containing cephalexin. The numbers of bacterial colonies were then counted. Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars.  , PXO99 only;
, PXO99 only;  , PXO99 plus niclosamide (distal);
, PXO99 plus niclosamide (distal);  , PXO99 plus niclosamide (local). Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in bacterial populations (**p < 0.001; ***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test) between niclosamide-treated local and systemic leaves at different time points after PXO99 inoculation.
, PXO99 plus niclosamide (local). Standard deviations of the means are indicated by vertical bars. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences in bacterial populations (**p < 0.001; ***p < 0.001; Student’s t-test) between niclosamide-treated local and systemic leaves at different time points after PXO99 inoculation.