Figure 3. γ-secretase proteolysis of Fra is required for Fra's ability to regulate comm expression.
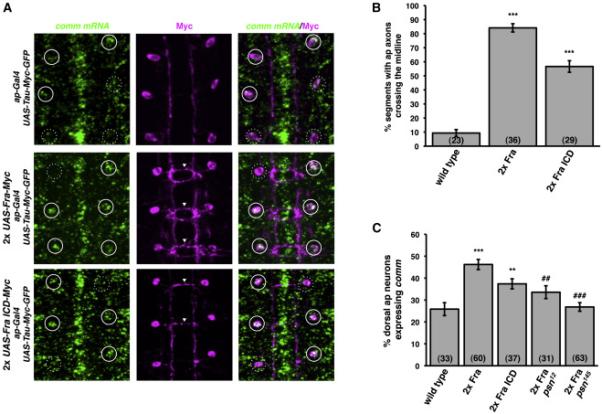
A) Fluorescent in situ hybridization for comm mRNA (green) in stage 17 embryos. Anterior is up. The cell bodies and axons of ap neurons are labeled with ap-Gal4 driving expression of UAS-Tau-Myc-GFP. Anti-Myc immunostaining is shown in magenta. White circles indicate the positions of dorsal apterous neuron cell bodies. Solid circles indicate ap neurons that express comm and dotted circles indicate ap neurons that do not express comm. Arrowheads indicate segments in which ap axons ectopically cross the midline.
B) Quantification of ap axon crossing in stage 16-17 embryos. Data were analyzed by ANOVA, followed by Student's t-test. *** indicates p<0.0001, compared to wild type embryos. Error bars indicate SEM. Number in parentheses indicates number of embryos scored. Note that the data for wild type embryos are also shown in Figure 5D.
C) Quantification of comm expression in dorsal ap neurons in stage 16-17 embryos. Data were analyzed by ANOVA, followed by Student's t-test. *** indicates p<0.0001, compared to wild type embryos. ** indicates p<0.005, compared to wild type embryos. ### indicates p<0.0001, compared to wild type embryos expressing two copies of Fra. ## indicates p<0.002, compared to wild type embryos expressing two copies of Fra. Error bars indicate SEM. Number in parentheses indicates number of embryos scored.
