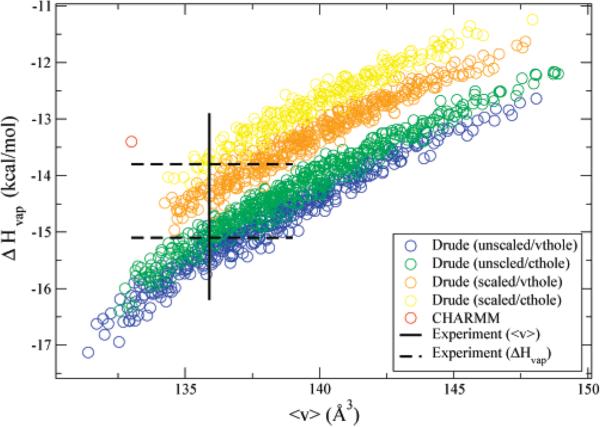
Figure 3.
The enthalpy of vaporization and molecular volume of neat liquid simulations for the four electrostatic models studied. Also included is the nonpolarizable CHARMM model. The simulations were run at T = 373 K. Each electrostatic model corresponds to a color. The individual circles of each electrostatic model type correspond to a different choice of LJ parameters. Each model gives interaction energies and geometries that agree to within 0.5 kcal/mol and 0.15 Å of QM calculations for the NMA–water dimer optimizations illustrated in Figure 2. The enthalpy of vaporization is calculated from the average change in energy upon formation of the dense system, ΔHvap = kT – (〈u〉liq - 〈u〉gas). Models that lie within 0.5 Å3 of the experimental molar volume (black box) were chosen for the next stage of the parametrization. Two estimates for the experimental enthalpy are illustrated.77,78