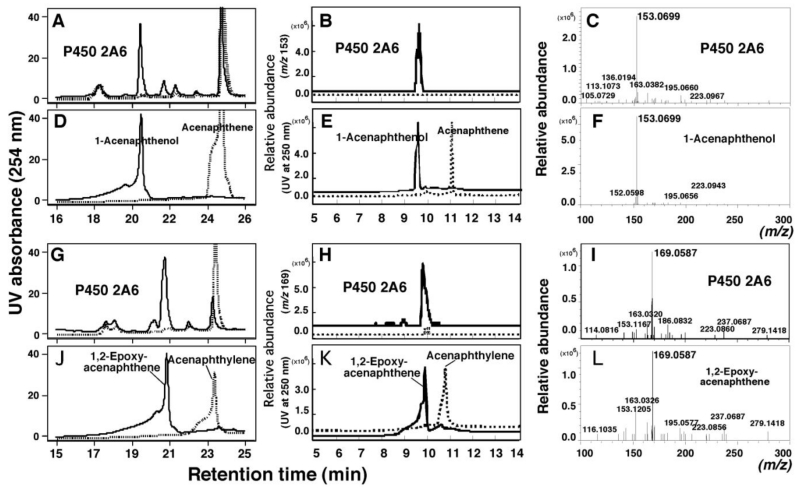
Figure 5.
HPLC and LC-MS analyses of oxidation of acenaphthene (A-F) and acenaphthylene (G-L) at 50µM substrate concentration by a bicistronic P450 2A6 system. HPLC analysis (by detecting at 254 nm) was carried out to determine the products of acenaphthene (A) and acenaphthylene (G) catalyzed by P450 2A6 in the presence (solid line) and absence (dotted line) of an NADPH-generating system. The standard acenaphthene and 1-acenaphthenol (D and E) and acenaphthylene and 1,2-epoxyacenaphthene (J and K) were analyzed using HPLC (D and J) and LC-MS (E and K). The same incubates were also analyzed with LC-MS at m/z 153.0783 (B) and 169.0649 (H) for detecting 1-acenaphthenol and 1,2-epoxyacenaphthene, respectively. MS analyses of a product of acenaphthene (C) and a 1-acenaphthenol standard (F) and of a product of acenaphthylene (I) and a 1,2-epoxyacenaphthene standard (L) were also determined.