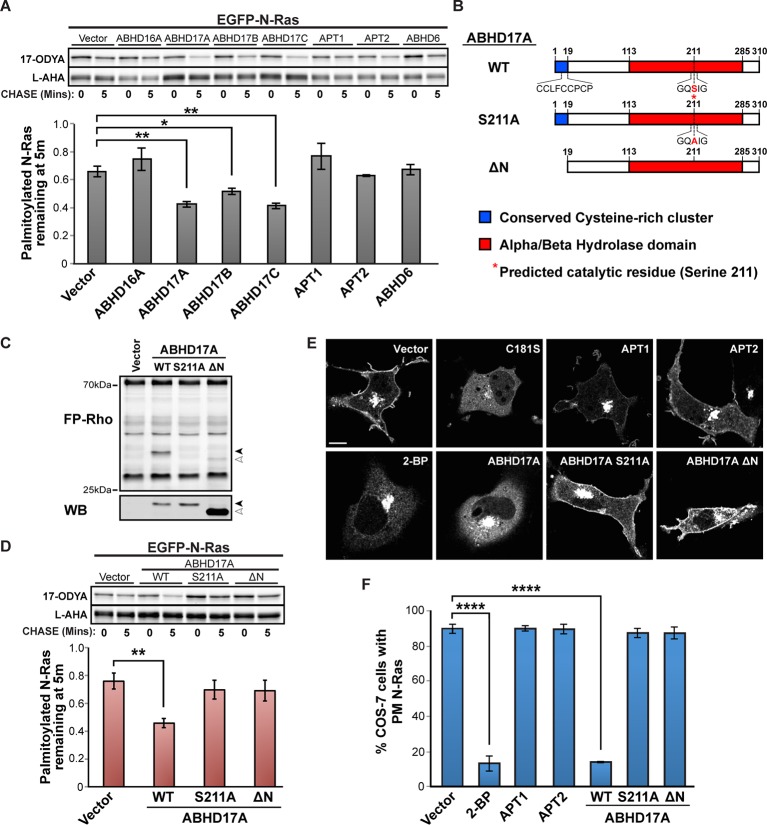
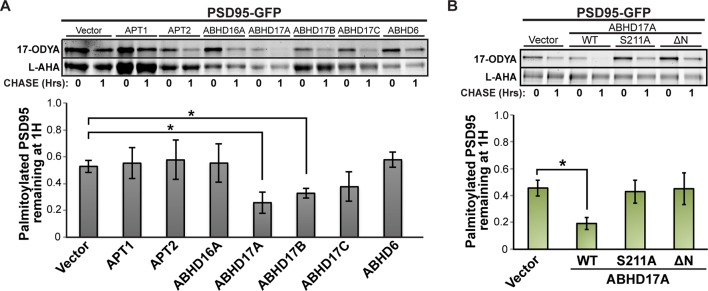
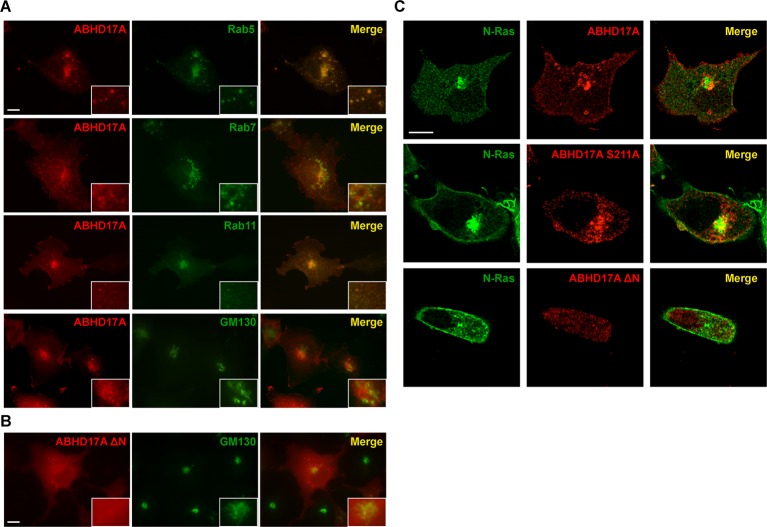
Figure 4. ABHD17A expression promotes N-Ras depalmitoylation and alters N-Ras subcellular localization.
(A) Pulse-chase analysis of N-Ras co-expressed with candidate mSHs as described in Figure 1. n = 3, mean ± SEM. (B) Schematic of the ABHD17A wild type, catalytically-inactive (S211A), and N-terminal truncation (ΔN) mutant proteins used in this study. (C) ABPP of ABHD17A wild type and mutant proteins by in-gel fluorescence (FP-Rho). Western blot (WB) shows proteins expressed in each condition. Filled arrowheads: ABHD17A WT and S211A; Open arrowheads: ABHD17A ΔN. (D) Pulse-chase analysis of N-Ras co-expressed with ABHD17A wild type and mutant proteins as described in Figure 1. n = 3, mean ± SEM. (E) Representative live confocal images of EGFP-N-Ras-C181S and EGFP-N-Ras localization in COS-7 cells treated with 100 μM 2-bromopalmitate (2-BP) or co-expressing the indicated thioesterases. Scale Bar = 10 μm. (F) Bar graph representing percentage of COS-7 cells with plasma membrane EGFP-N-Ras under each condition studied in (E). n = 3 (100 cells counted per trial), mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001. mSHs, metabolic serine hydrolases; SEM, standard error of the mean.