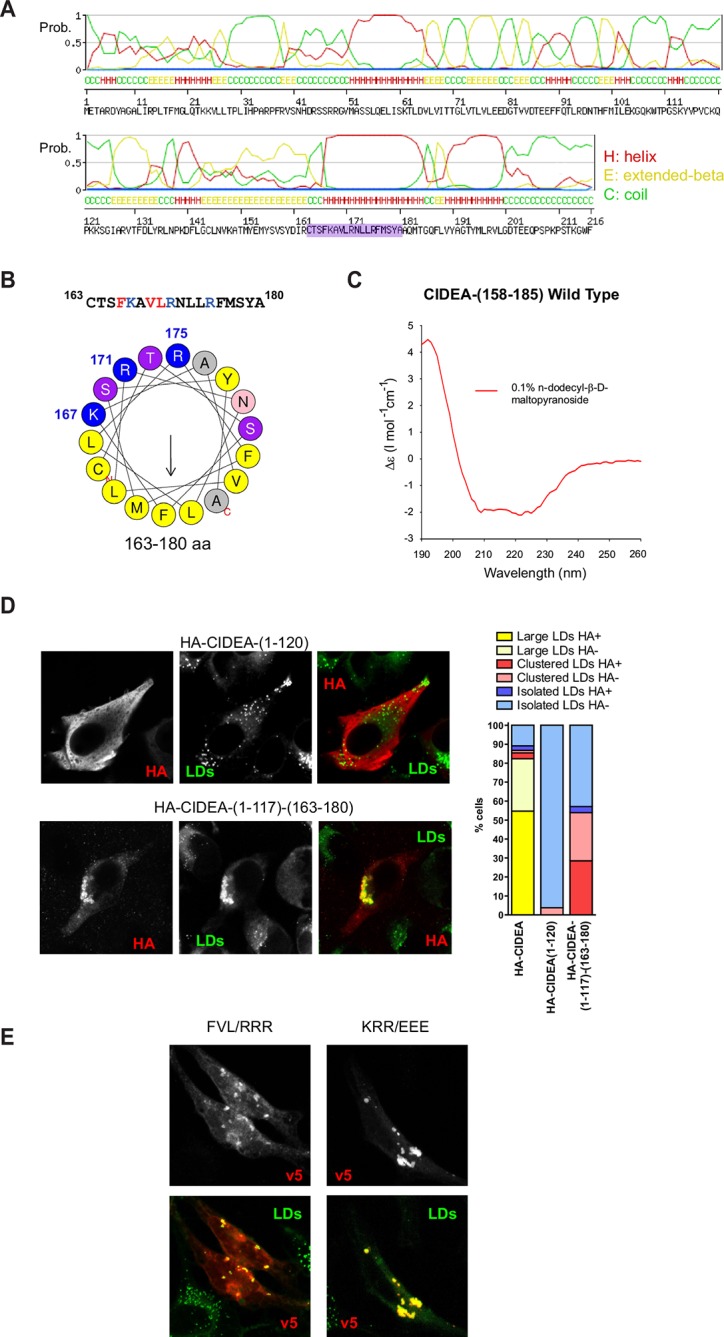
Figure 3. CIDEA targets the LD monolayer through a cationic amphipathic helix.
(A) Secondary structure of CIDEA predicted by SWISS-MODEL server. (B) Helical wheel representation of the putative amphipathic α-helix (163–180) generated at http://heliquest.ipmc.cnrs.fr/. (C) Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of a 28-aa peptide corresponding to the 158–185 sequence of CIDEA (41 μM) solubilized in 50 mM potassium phosphate, pH 6.2 plus 0.1% n-dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside. (D) A Hela cell expressing HA-CIDEA-(1–120)-v5 (red) or HA-CIDEA-(1–117)-(163–180) (red), showing the inclusion of aas 163–180 enhances LD localization and the ability to promote LD docking. The phenotypic distribution was performed in a minimum of three independent experiments for every construct (n>50 cells). HA signal in LDs was only detected in a proportion of the cells where HA-CIDEA constructs had induced LD enlargement or clustering, possibly due to the formation of CIDEA complexes reducing antibody accessibility to the HA epitope at the N-term. (E) A Hela cell expressing CIDEA-(F166R/V169R/L170R)-v5 (red) showing aa substitutions to compromise amphipathicity of the helix disrupt LD targeting, and a Hela cell expressing CIDEA-(K167E/R171E/R175/E)-v5 (red) showing amino acid (aa) substitutions to invert the charge of the helix but maintaining amphipathicity retains predominantly LD localization.