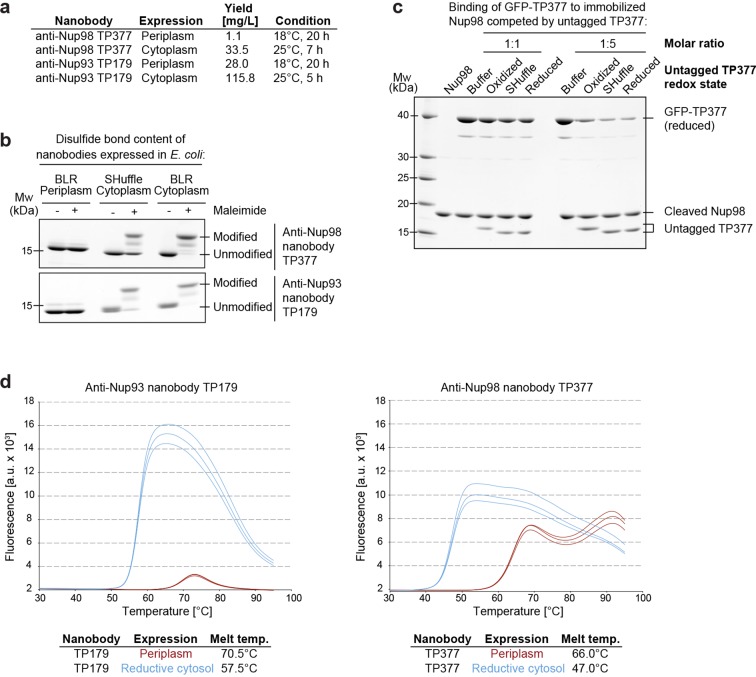
Figure 1. Affinity and thermostability of reduced and oxidized nanobodies.
(a) Comparison of typical yields for the anti-Nup93 nanobody TP179 and the anti-Nup98 nanobody TP377 expressed either in the Escherichia coli BLR periplasm with a C-terminal His6-tag or in the oxidative cytoplasm of E. coli SHuffle with an N-terminal His14-bdNEDD8-tag. (b) Analysis of disulfide bond content using a maleimide shift assay. Anti-Nup93 nanobody TP179 and anti-Nup98 nanobody TP377, expressed either in the oxidative periplasm of E. coli BLR, the oxidative cytosol of E. coli SHuffle or in the reductive cytoplasm of E. coli BLR, were subjected to modification with biotin-PEG23-maleimide in SDS–PAGE sample buffer (-DTT) and analyzed by non-reducing SDS–PAGE followed by Coomassie staining. (c) The redox state of the anti-Nup98 nanobody TP377 does not affect the affinity for its target. Biotinylated His14-Avi-bdSUMO-tagged Nup98716-866 was immobilized on Streptavidin agarose und used to bind the reduced GFP-tagged TP377. Binding was in the absence or presence of an equimolar amount or fivefold excess of nanobody competitor, namely untagged TP377 produced either in the oxidative periplasm, in the mildly oxidative cytoplasm of E. coli SHuffle or in the reductive cytoplasm of BLR. Bound nanobodies were then eluted by proteolytic cleavage of the bdSUMO tag of Nup98 and analyzed by SDS–PAGE followed by Coomassie staining. Note that the oxidized, disulfide bond-stabilized nanobody (produced in the periplasm) behaved like the reduced variant (produced in the E. coli BLR cytoplasm). Formation of the disulfide bond therefore does not seem to significantly contribute to the overall affinity. (d) Differential scanning fluorimetry (thermofluor, Niesen et al., 2007) analysis of nanobodies expressed in the oxidative periplasm (red) or the reductive cytosol (blue) of E. coli BLR. The anti-Nup93 and anti-Nup98 nanobodies were heated in the presence of Sypro Orange dye from 30 to 100°C and thermal unfolding curves were obtained. The melting temperature is derived from the inflection point of the curve.