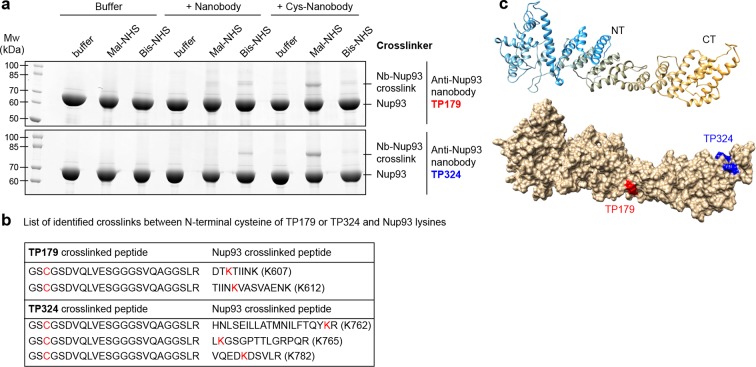
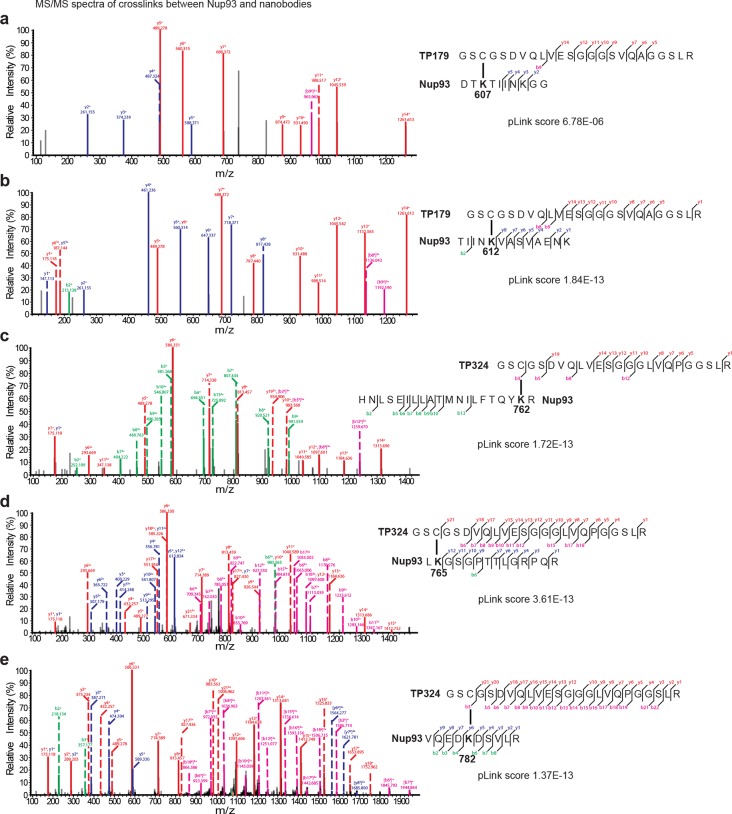
Figure 8. Rapid epitope mapping via crosslinking mass spectrometry.
(a) Crosslinking of two different anti-Nup93 nanobodies (TP179 and TP324) to Nup93 using amine-to-amine ('Bis-NHS'; BS3; 11.4 Å linker length) or thiol-to-amine ('Mal-NHS'; BMPS; 5.9 Å linker length) crosslinking reagents. The combination of the very short Mal-NHS crosslinker with an engineered cysteine close to the antigen-binding loops provided for both nanobodies by far the highest yield of crosslinked nanobody•Nup93 adduct. (b) List of identified crosslinked peptides involving Nup93 lysines and Cys-TP179 or Cys-TP324. The crosslinked amino acids are highlighted in red (see also Figure 8—figure supplement 1). (c) Crosslinked lysines of Nup93 to the N-terminal cysteine on anti-Nup93 nanobodies TP179 (red) or TP324 (blue) are depicted on a structural model of Nup93168-end generated by I-TASSER (Zhang, 2008). Based on the orthologous yeast crystal structures (Jeudy and Schwartz, 2007; Schrader et al., 2008), Nup93 is predicted to form a similar J-shaped structure (color gradient: NT = N-terminus in blue to CT = C-terminus in orange). Whereas TP179 binds to the central portion, TP324 binds to the C-terminus of Nup93.