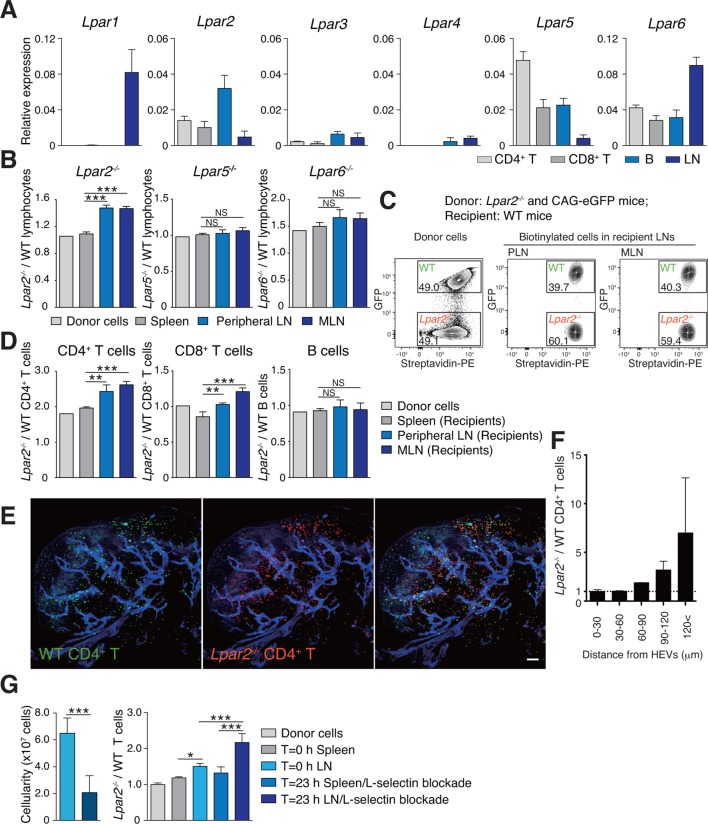
Figure 4. Lpar2 deficiency causes T cells to be retained in LNs.
(A) LPA-receptor expression in lymphocyte subsets: CD4+ T, CD8+T, B cells and whole LNs were analyzed by real-time RT-PCR; expression levels were normalized to Gapdh. Data shown are representative of three individual experiments. (B–D) Migration of LPA receptor–deficient lymphocytes into secondary lymphoid tissues. Splenocytes from eGFP-expressing mice and from Lpar2-/-, Lpar5-/-, or Lpar6-/- mice were mixed in equal numbers, labeled with biotin, and injected intravenously into WT recipients. After 1.5 hr, secondary lymphoid tissues were collected from the recipient mice and donor-derived lymphocytes were detected with flow cytometry. (B) Ratio of LPA receptor-deficient (Lpar2-/-, Lpar5-/- or Lpar6-/-) cells to eGFP-expressing (WT) cells that migrated into the spleen, peripheral LN, and MLN after adoptive transfer into WT recipient mice. (C) Representative dot plots of donor cells (before transfer) and biotinylated cells in LNs of recipient mice (after transfer). (D) Lpar2-/- lymphocyte subpopulations that migrated into the spleen, peripheral LN, and MLN of recipient mice. Data shown for adoptive transfer experiments using Lpar2-/-, Lpar5-/- and Lpar6-/- lymphocytes are representative of five, two, and three independent experiments, respectively (n=4 mice per group). (E, F) Localization of adoptively transferred WT and Lpar2-/- CD4+T cells in LNs. DiD-labeled CD4+ T cells from WT mice (1 x 107 cells, pseudocolored in green) were mixed equally with CMTMR-labeled Lpar2-/- CD4+ T cells (red) and injected intravenously into WT recipient mice; 90 min later, Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated MECA-79 mAb (pseudocolored in blue) was injected intravenously to visualize HEVs. (E) LNs were collected and analyzed by confocal microscopy. (F) The distance that CD4+ T cells migrated from HEVs was measured, and the ratio of Lpar2-/- to WT T cells was calculated. Data represent mean ± SD from 3 mice. Data are representative of two (E, F) independent experiments. (G) Ratio of Lpar2-/- T cells to WT T cells retained in LNs when lymphocyte entry into LNs was blocked. CFSE-labeled CD45.1+ WT and CD45.2+Lpar2-/- CD4+ T cells were intravenously injected into CD45.2+ WT mice. Two hours later, anti-L-selectin antibody (MEL-14) was injected (T = 0 hr). At T=0 hr and T=23 hr, the total cell number in LNs (left) and the frequency of donor-derived cells (right) were measured. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. Data represent the mean ± SD (A, B, D, F, G). Differences between groups were evaluated by one-way ANOVA (B, D, G [right]) or Student’s t-test (G [left]). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005. Bars: 100 μm.