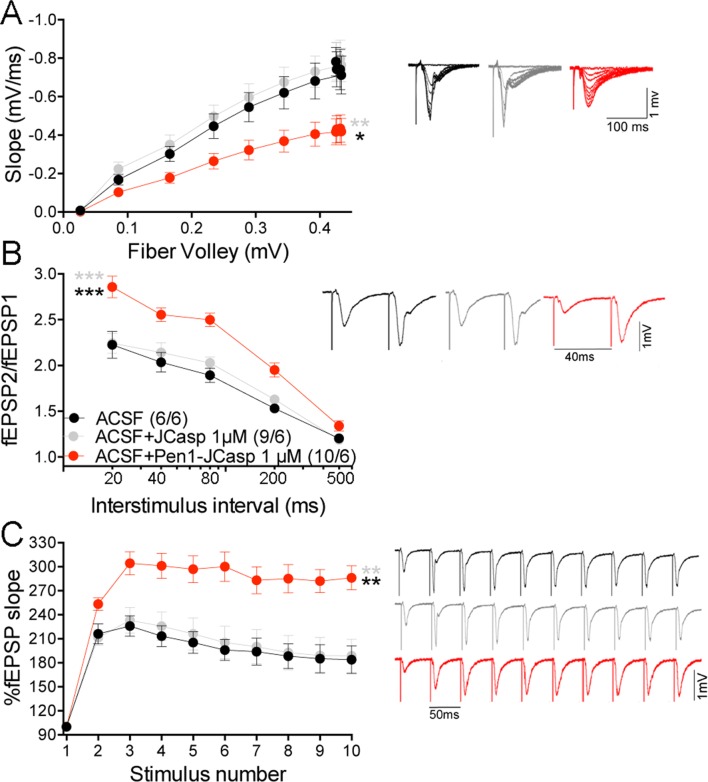
Figure 7. Pen1-JCasp impairs excitatory synapses via an intracellular mechanism.
Pen1-JCasp, but not JCasp, reduces basal synaptic transmission (A) paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) (B) and frequency facilitation (FF) at 20 Hz (C). Representative traces are shown. Stimulus artifacts are removed from the FF traces for clarity. The number of recordings and of mice analyzed are shown in (B). Statistical assessments were performed by: one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test for slopes of input/output (I/O) curves; two-way repeated measures (RM) ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test for PPF and FF. *Pen1-JCasp 1 μM vs. artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF), *Pen1-JCasp 1 μM vs. JCasp; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. The complete statistical analyses are shown in the attached Excel file. All data represent means ± SEM.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.09743.019