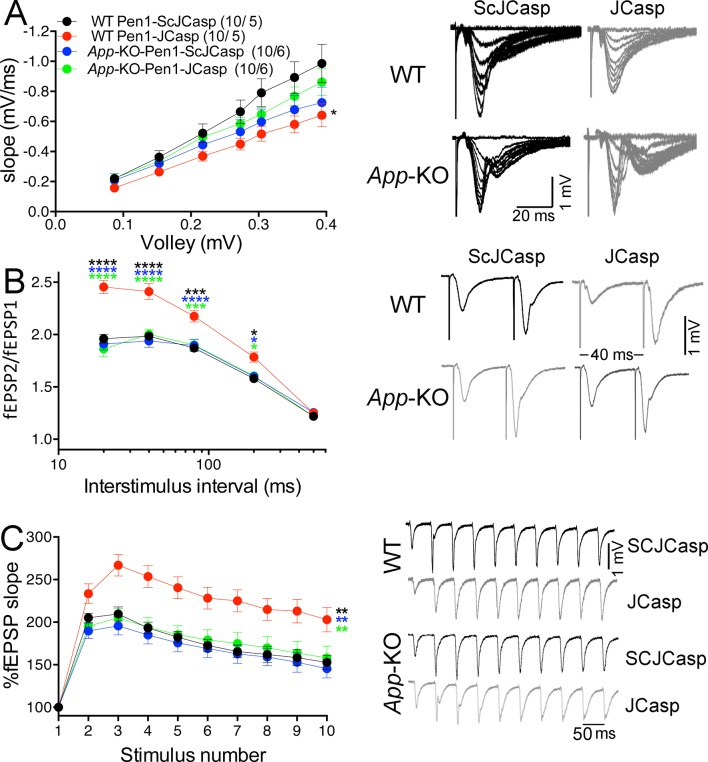
Figure 9. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is required for the inhibitory effect of Pen1-JCasp on synaptic transmission.
(A) Analysis of slopes of each input/output (I/O) recording by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test showed no significant differences among the groups. However, uncorrected Fisher’s LSD test shows that Pen1-JCasp reduces basal synaptic transmission in wild-type (WT) hippocampal slices as compared to WT slices treated with Pen1-ScJCasp. Pen1-JCasp increases paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) (B) and frequency facilitation (FF) (C) in WT but not App-KO excitatory Schaffer collateral (SC) synapses. Representative traces are shown on the right of summary plots. The number of recordings and of mice analyzed for each group are shown in (A). All data represent means ± SEM. Statistical assessment by two-way repeated measures (RM) ANOVA shows significant differences in PPF and FF between WT mice treated with Pen1-JCasp and the other three experimental groups (*, vs. WT+Pen1-SCJCasp; *, vs. App-KO+Pen1-SCJCasp; *, vs. App-KO+Pen1-JCasp; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001). The complete statistical analyses are shown in the attached Excel file.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.09743.025