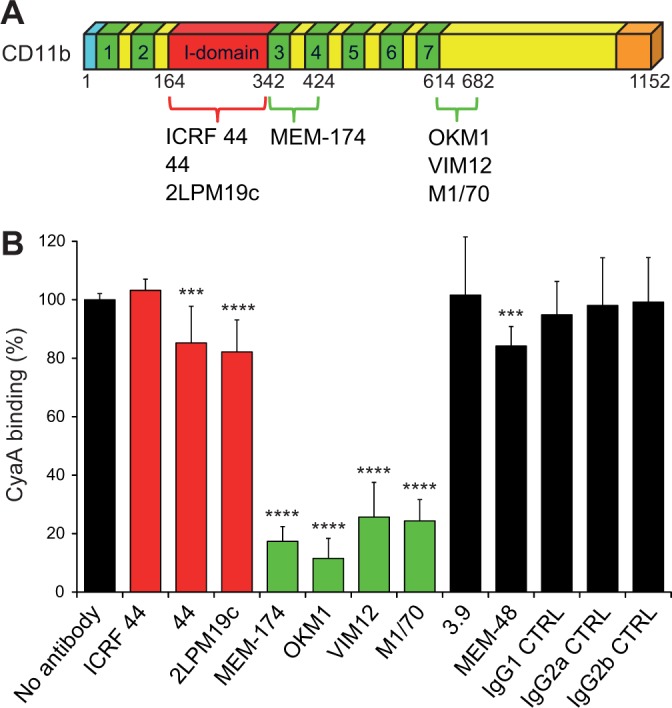
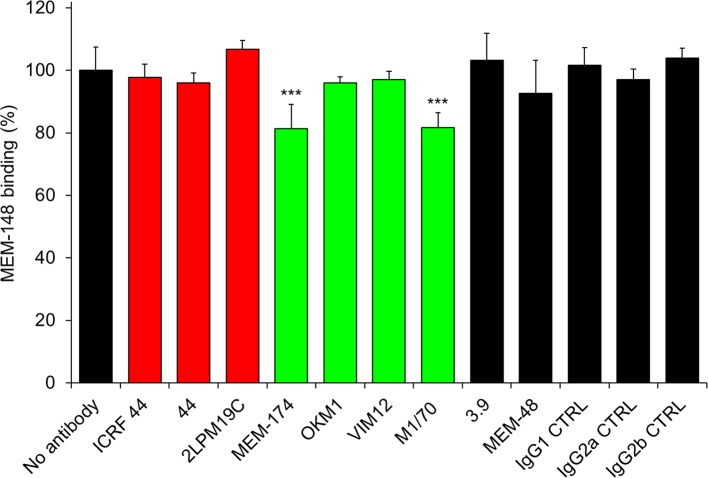
Figure 2. Antibodies recognizing the same segments of CD11b as CyaA block its binding to CR3.
(A) Schematic representation showing the binding segments of a set of mAbs in the CD11b subunit of CR3, which were mapped by flow cytometry. The ICRF 44, 44 and 2LPM19c mAbs recognize the I-domain of CD11b, the major ligand binding site of CR3. The MEM-174, or OKM1, VIM12 and M1/70 mAbs target amino acid segments 342-424 or 614-682 of CD11b, respectively, which are important for CyaA binding. (B) 2x105 CHO-CD11b/CD18 cells were preincubated without or with saturating concentrations of different mAbs and then incubated with 2 µg/ml of CyaA-biotin. Surface-bound CyaA-biotin was labeled with streptavidin-PE and the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. CyaA binding was expressed as percentage of toxin binding to CHO-CD11b/CD18 cells treated without mAb. Each bar represents the mean value with SD of at least eight determinations from at least three independent experiments. Significant differences between mean values of CyaA binding to mAb-untreated cells and cells treated with different mAbs are indicated (***, p<0.001; ****, p<0.0001; ANOVA). 3.9, CD11c-specific mAb; MEM-48, CD18-specific mAb; IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b, isotype control mAbs.