Figure 9. CyaA binds and intoxicates cells expressing LFA-1 with equally low efficacy as cells expressing CR4, or lacking any β2 integrin at all.
(A) 2x105 stably transfected CHO cells expressing CD11a-YFP/CD18, CD11b-YFP/CD18, CD11c-YFP/CD18, or no β2 integrin were incubated with different concentrations of Dy647-labeled intact CyaA and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean fluorescence intensities of CyaA binding were plotted against the concentrations of CyaA. RFI, relative fluorescence intensity. (B) 1x105 CHO cells expressing integrin molecules were incubated at indicated concentrations of CyaA and the amounts of accumulated cAMP were determined in cell lysates by ELISA. (A and B) Each point represents the mean value ± SD of three independent experiments performed in duplicate. CyaA binding to or cAMP intoxication of cells expressing CD11a-YFP/CD18, CD11c-YFP/CD18, or no β2 integrin was at all toxin concentrations significantly lower than toxin binding to or cAMP intoxication of cells expressing intact CD11b-YFP/CD18 (p<0.0001; ANOVA). However, CyaA binding to or cAMP intoxication of cells expressing CD11a-YFP/CD18 was at all measured toxin concentrations found to be statistically the same as toxin binding to or cAMP intoxication of cells expressing CD11c-YFP/CD18 or no β2 integrin at all (P > 0.1; ANOVA).

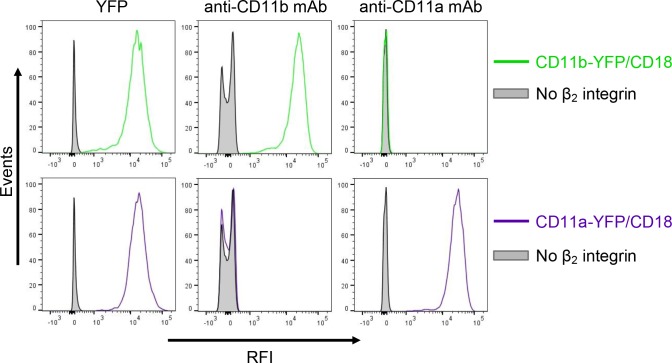
Figure 9—figure supplement 1. Expression of integrin variants fused with a fluorescent YFP protein on the surface of CHO cells.
Figure 9—figure supplement 2. Residual binding of CyaA to CD11a-YFP/CD18 is not due to the presence of the YFP tag.
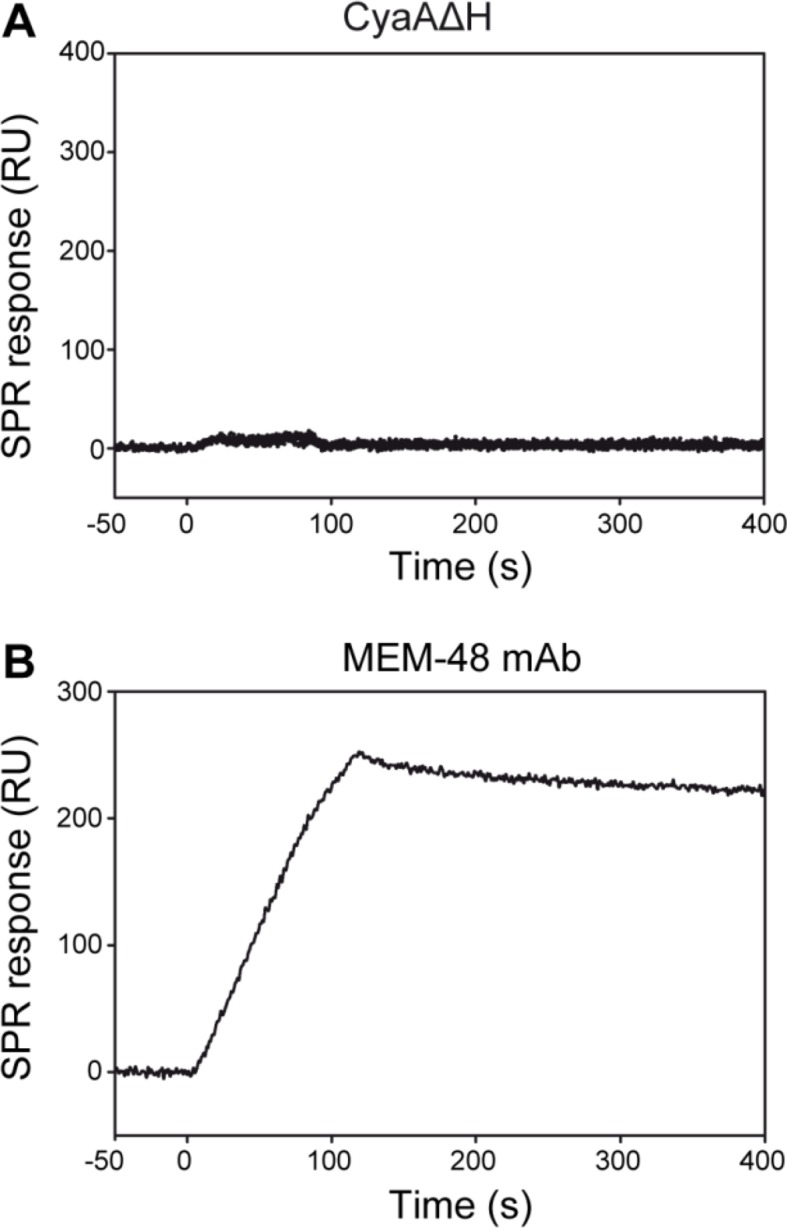
Figure 9—figure supplement 3. CyaA does not interact with the intact native LFA-1 integrin.