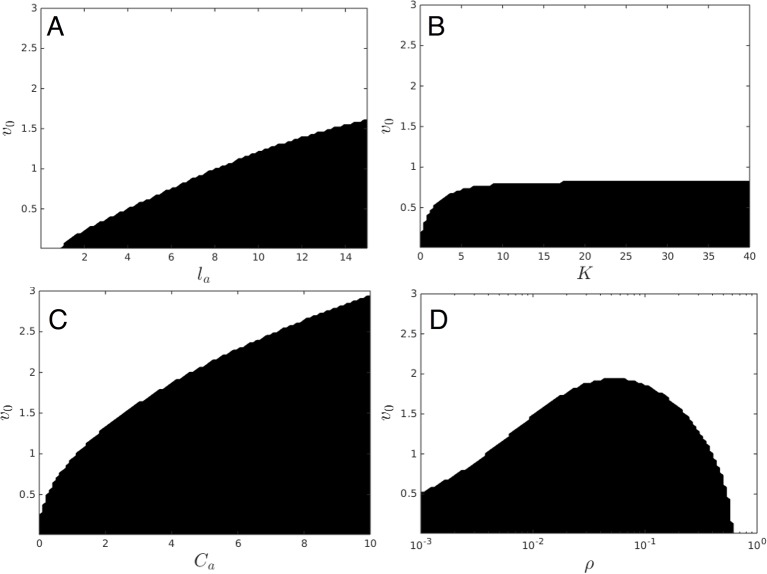
Appendix figure 10. Regions of parameter space where dispersed state is stable (white) and unstable (black).
Instability of dispersed state causes transition to cohesive state. (A) Sensitivity to la, for ρ = .0025, K = 25, lr = 1.0, Ca = 1.0, Cr = 1.1. Increasing la promotes instability and formation of the cohesive state, as does decreased v0. (B) Sensitivity to K, for ρ = .0025, la = 7.5, lr = 1.0, Ca = 1.0, Cr = 1.1. Increasing K promotes instability and formation of the cohesive state, as does decreased v0. Large values of K lead to roughly the same stability properties, due to the exponential decay of the interaction with length. (C) Sensitivity to Ca, for ρ = .0025, la = 7.5, lr = 1.0, K = 25, Cr = 1.1. Increasing Ca promotes instability and formation of the cohesive state, as does decreased v0. (D) Sensitivity to ρ. Smaller v0 promotes instability. When ρ is very small, increasing ρ makes instability more likely.