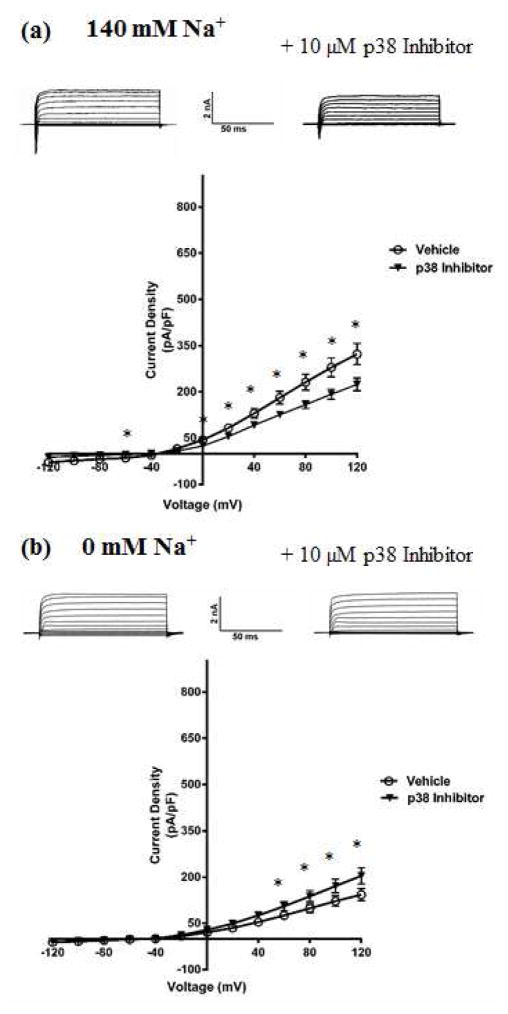
Fig. 3. DRG neurons have decreased KNa component of IK current upon inhibition of p38 MAPK.
(a) Top- Representative traces from whole-cell recordings of DRG neurons treated with 10 μM p38 Inhibitor for 90 minutes at 37 °C, in bath solution containing sodium. Bottom, Current-Voltage relationship of IK measured from p38 Inhibitor-treated DRG neurons in bath solution containing sodium. (b) Top- Representative traces from whole-cell recordings of DRG neurons treated with 10 μM p38 Inhibitor for 90 minutes at 37 °C, in bath solution containing the impermeant cation NMG in place of sodium. Bottom, Current-Voltage relationship of the isolated KNa current measured from Inhibitor-treated DRG neurons in bath solution containing NMG. Holding potential was −70 mV, and currents were elicited with voltage steps from −120 mV to +120 mV in 20 mV increments. Data are means ± SEM (n=8–12 per group). Statistical analysis was done using Student’s unpaired t-test (*p<0.05).