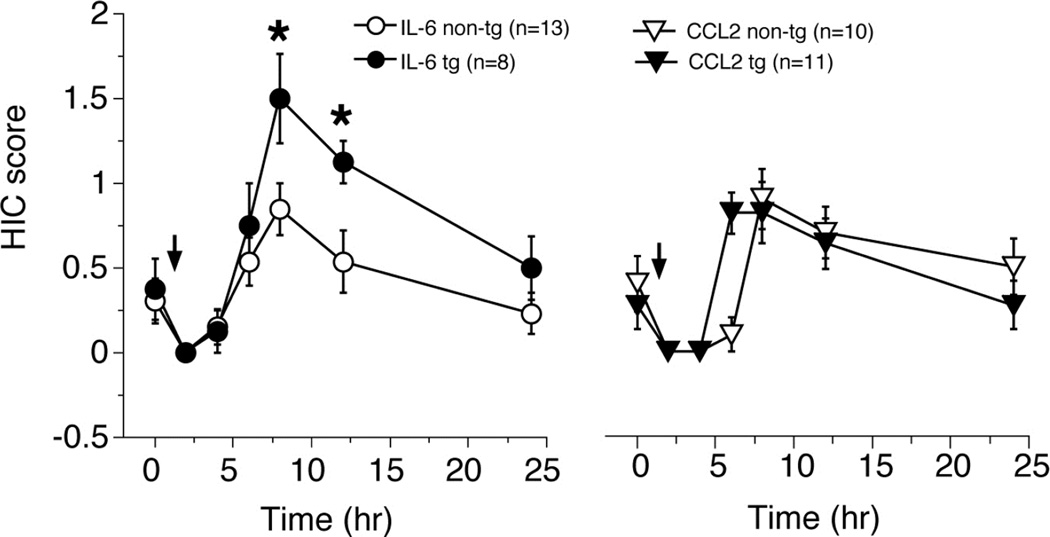
Figure 6.
IL-6 tg mice showed a higher level of CNS excitability during withdrawal from acute ethanol as measured by HIC assay. Graph showing mean values (±SEM) for HIC scores measured over a 24 hr period in IL-6 tg (closed circles) and non-tg (open circles) mice and CCL2 tg (closed triangle) and CCL2-non-tg (open triangle) mice. Mice were given a high dose of ethanol (4 gm/kg, i.p.) and tested at several different time points. The IL-6 tg mice showed significantly higher peak HIC scores than their non-tg littermates. No genotypic difference was observed for the CCL2 tg and non-tg mice. Baseline HIC scores were similar for all genotypes, as were the scores for initial time points (2,4, and 6 hr) following ethanol administration (arrow). *Significantly different from non-tg mice (Repeated measure ANOVA with post hoc Fisher’s PLSD, p<0.05). @Significantly different from baseline values for the same genotype (paired t-test, p<0.05).