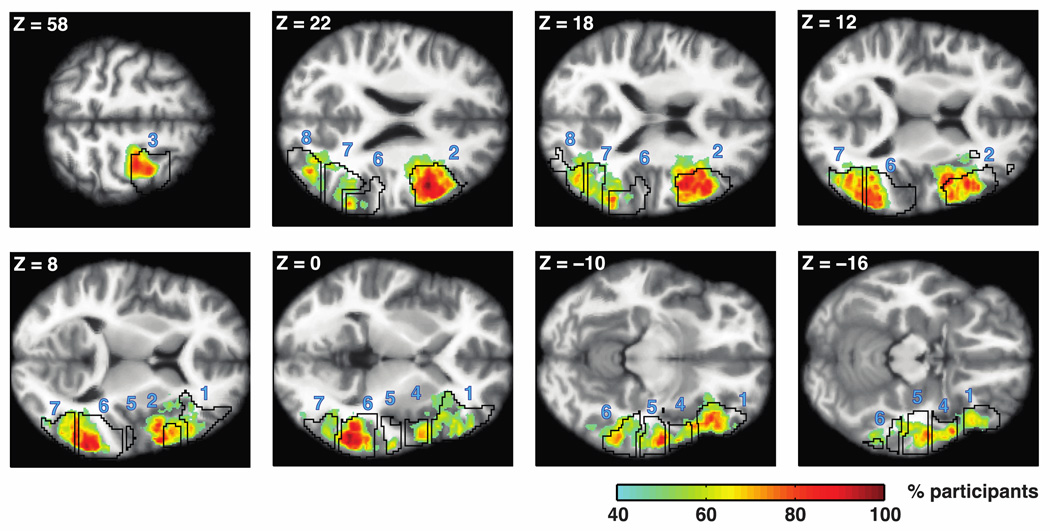
Figure 7.
Overlap across participants in the anatomical location of the syntactic complexity effect. Heat maps depict voxels in which more than 40% of participants have an “activation neighborhood” for the syntactic complexity contrast (object-extracted > subject-extracted). Neighborhoods were defined as maximal sets of contiguous voxels that surrounded an activation peak and had contrast estimates numerically greater than zero. Black contours depict our group-based masks (from Fedorenko et al., 2010) used to define fROIs. Numbers correspond to the order of fROIs in Figure 4: 1, LIFGorb; 2, LIFG; 3, LMFG; 4, LAntTemp; 5, LMidAntTemp; 6, LMidPostTemp; 7, LPostTemp; 8, LAngG. Data are superimposed on horizontal slices of Freesurfer’s average T1 scan in common MNI space. Slices were chosen to maximize visibility of the greatest overlap in each mask. Note the especially high overlap (shown in dark red) in the LIFG and LMidPostTemp.