Figure 1.
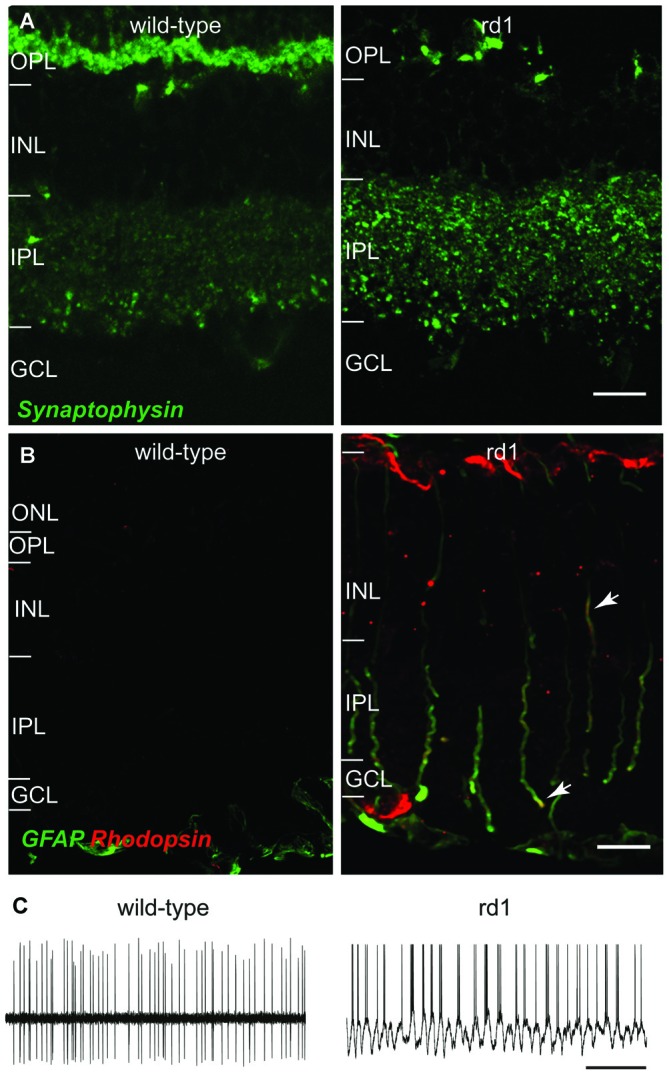
Representative changes in retina following photoreceptor loss in rd1 mouse retina. (A) Loss of photoreceptors results in upregulation of synaptic proteins in inner retina. Vertical retinal sections of adult wild-type (left) and rd1 (right) mouse retinas showing synaptophysin expression in OPL and IPL. Synaptophysin is nearly absent in the OPL, because the photoreceptor terminals have degenerated; however, synaptophysin expression is increased in the IPL. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Loss of photoreceptors in rd1 mouse causes several changes in Müller glial cells, including expression of several mature neuronal proteins. Vertical sections of wild-type (left) and rd1 (right) mouse retinas showing the expression of rhodopsin (red) in the GFAP-positive (green) Müller glia of rd1 mouse (arrows point to Müller cell processes expressing both GFAP and rhodopsin [yellow]). Scale bar: 10 μm. (C) The changes in inner retinal circuitry lead to oscillatory activity in RGCs. Representative spontaneous spike trains from RGCs in wild-type (left; extracellular recording) and rd1 (right; whole cell recording) mouse retinas showing oscillatory spiking in the rd1 mouse retina. Scale bar: 1 s. Images in (A,B) are adapted with permission from Dagar et al. (2014) and Goel and Dhingra (2012), respectively.
