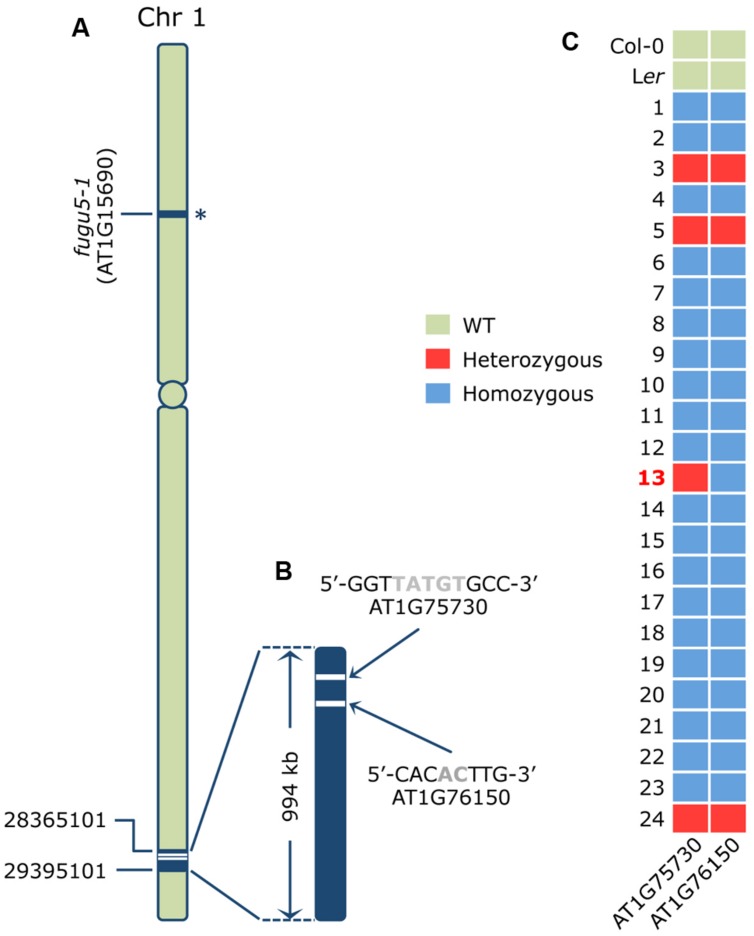
FIGURE 2.
Identification of the causative mutation in the A#3-1; fugu5-1 mutant. (A) Schematic representation of chromosome 1 of Arabidopsis thaliana where the AVP1/FUGU5 locus harboring the molecular lesion in the loss-of-function fugu5-1 allele is indicated by an asterisk. Map-based cloning mapped the A#3-1; fugu5-1 causative mutation to the lower arm of chromosome 1 between positions 28365101 and 29395101, as indicated. (B) Whole genome sequencing data of A#3-1sm genomic DNA and rough mapping identified two mutations within a 994 kb mapping interval. The two candidate mutations were a 5-bp deletion (TATGT at position 28436746-28436750 causing a frame shift) in exon 9 of the AT1G75730 gene encoding a protein of unknown function, and a 2-bp deletion (AC at the 28575546-28575547 position causing a frame shift) in exon 10 of the AT1G76150/ECH2 gene encoding the monofunctional proxisomal ENOYL-COA HYDRATASE 2. (C) To determine which of these two mutations is responsible for the A#3-1 phenotype, an additional 21 F2 individual homozygous for the A#3-1sm phenotype and three F2 individuals heterozygous for the A#3-1sm phenotype were subjected to genotyping by high-resolution melting (HRM) curve analysis as described previously (Kazama et al., 2011). The nucleotide sequences of the specific primer sets used for HRM are indicated in the Section “Materials and Methods.”