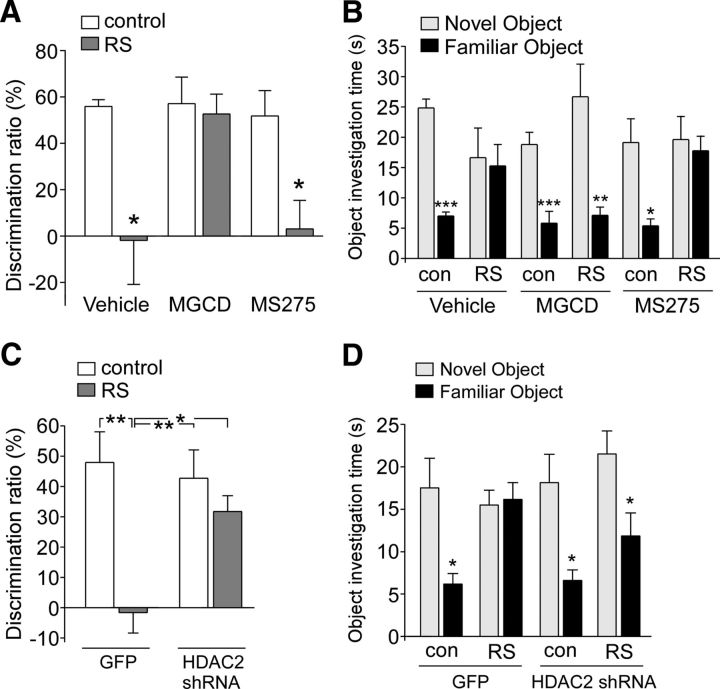
Figure 5.
HDAC2 inhibition or knock-down blocks the effect of repeated stress on TOR memory. A, Bar graphs showing the DR of TOR tasks in control (con) versus repeatedly stressed (RS) rats with the intraperitoneal injection of vehicle, MGCD0103 (15 μg/kg), or MS-275 (15 μg/kg). *p < 0.05, ANOVA. B, Bar graphs showing the exploration time for novel versus familiar objects in the test trial of TOR tasks in control (con) versus repeatedly stressed animals with the intraperitoneal injection of vehicle, MGCD0103 (15 μg/kg), or MS-275 (15 μg/kg). ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, t test. C, Bar graphs showing the DR of TOR tasks in control versus repeatedly stressed animals injected with GFP or HDAC2 shRNA lentivirus. **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05, ANOVA. D, Bar graphs showing the exploration time for novel versus familiar objects in the test trial of TOR tasks in control (con) versus repeatedly stressed animals with PFC injection of GFP or HDAC2 shRNA lentivirus. *p < 0.05, t test.