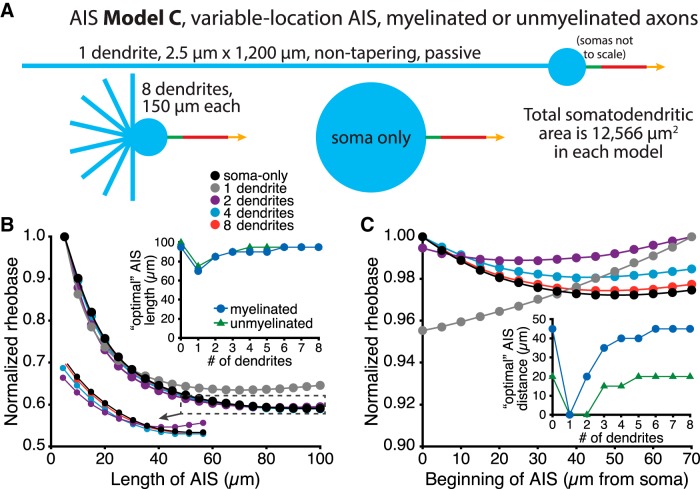
Figure 10.
Impact of dendritic topology on AIS performance. A, Diagrams of ball-and-stick model neurons (AIS Model C) having zero, one, or eight nontapering (2.5 µm diameter) passive dendrites that conserve a total somatodendritic surface area of 12,566 µm2 in each model. In the soma-only model, the densities of active somatic conductances were reduced in the enlarged soma to conserve the same total conductances present in the baseline soma. B, Plots of normalized rheobase currents for different AIS lengths (AIS Model A; conserved sodium and potassium conductance densities) in model neurons having variable somatodendritic topology, but conserved total surface areas. Top inset, Plots of optimal AIS length vs the number of dendrites in models having preserved total somatodendritic surface area. Bottom inset, An expanded view of the indicated data points. C, Plots of normalized rheobase currents for the same model neurons having a 30-µm-long AIS placed at the indicated distances from the soma (AIS Model C). Inset, Plots of optimal AIS distance from the soma vs the number of dendrites in models having preserved total somatodendritic surface area.