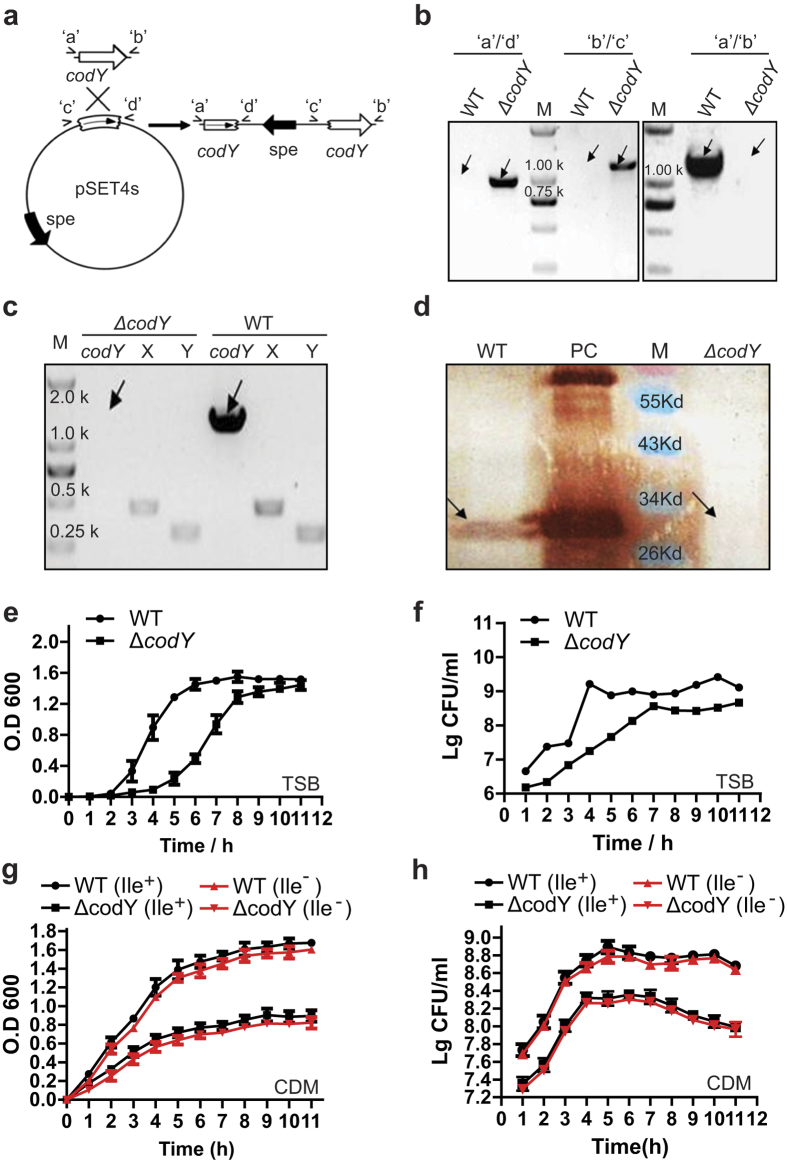
Figure 1. Construction of the codY mutant strains and growth curves of the wild-type (WT) and ∆codY strains.
(a) Strategy for the mutation of codY in S. suis SC19 by homologous recombination. PCR was used to amplify the codY DNA fragment, which was cloned into the pSET4s vector to produce pSET4s-codY’ which was used for the codY gene insertion mutation. ‘c’ and ‘d’ indicate the left and right homologous arms of codY. (b) PCR confirmation of the mutant strains. The primer pairs used in the PCR analysis are indicated above the lanes. Genomic DNAs from the wild type (WT) and codY mutation (∆codY) strains were used as templates. (c) RT-PCR confirmed that the only WT expressed the codY mRNA. (d) Western blotting was used to confirm that the expression of CodY (predict size of 29.3 kDa) was disrupted in the ∆codY strain. M, the Pre-stained protein marker with the indicated sizes; an arrow shows the predicted CodY band position. PC, Positive Control, purified CodY protein expressed by E. coli BL21(DE) from vector pET-28a-codY-His. (e–h) Effect of the codY mutation on the growth of S. suis 2, which was evaluated by OD 600 and CFU counting at indicated time points in TSB medium with isoleucine (Ile+) (e,f) or in the chemically defined medium (CDM) with (Ile+) or without isoleucine (Ile−) (g,h), respectively. WT (Ile+) and WT (Ile−) , wild type strain cultured in CDM with or without isoleucine; ∆codY (Ile+) and ∆codY (Ile−), codY mutation strain cultured in CDM with or without isoleucine. Each curve shown is representative of a typical experiment that was performed three times. Each curve shown isrepresentative of a typical experiment that was performed three times.