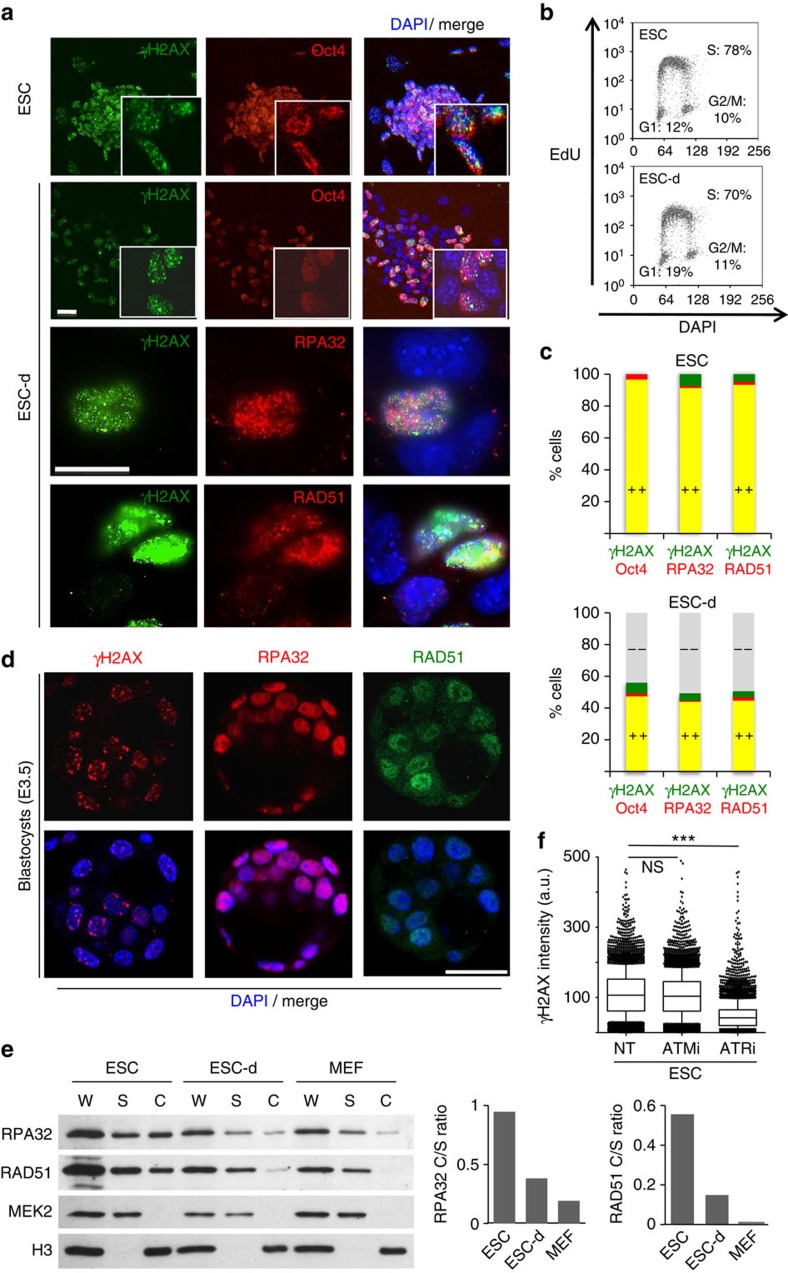
Figure 1. Replication stress markers are present in vitro in ESCs and in vivo in ICM cells.
(a) Immunofluorescence (IF) staining of an embryonic stem cell (ESC) colony and partially differentiated ESCs (ESC-d; 3d from LIF removal) for the stem cell marker Oct4, the DNA damage marker γH2AX and chromatin-bound ssDNA-binding proteins RPA32 and RAD51. Scale bars, 25 μm. (b) FACS analysis of EdU incorporation and DNA content (DAPI) in ESC and ESC-d. The percentage of cells in the different cell cycle phases is indicated. (c) Quantification of double IF-stainings displayed in a) in ESC and ESC-d. A minimum of 150 cells were scored in each double staining. (d) IF staining for γH2AX, RPA32 and RAD51 of E3.5 blastocysts. Number of embryos analysed per staining was 12, 11 and 9, respectively. Representative images are shown (see also Supplementary Figs 2 and 3). Scale bar, 25 μm. (e) Immunoblot detection of the indicated proteins after biochemical fractionation performed on ESC, ESC-d and mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Cytosolic kinase MEK2 and chromatin-bound H3 serve as fractionation controls. Original films were scanned at high resolution and the intensity of immunoblot signals was quantified with ImageJ. C, chromatin-enriched fraction; S, soluble fraction (includes cytosol and abundant nucleosoluble proteins); W, whole-cell extract. Histograms represent chromatin/soluble (C/S) ratios for RPA32 (left) and RAD51 (right). (f) FACS-based quantification of γH2AX staining in ESCs on mock, ATM inhibitor (ATMi) or ATR inhibitor (ATRi) treatment. All these experiments were performed in duplicate. a.u., arbitrary units.