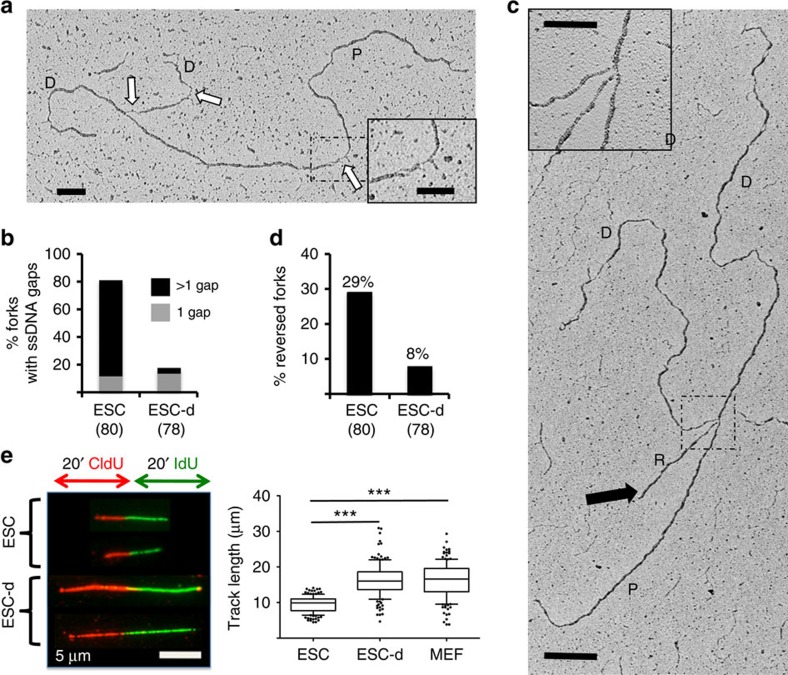
Figure 2. ESCs display massive accumulation of ssDNA gaps, reduced fork speed and frequent fork reversal.
(a,c) Electron micrographs of representative replication forks from ESCs, with indicated parental (P) and daughter (D) duplexes. White arrows indicate ssDNA gaps; black arrow points to the regressed arm (R) of a reversed fork. Insets: (a), a magnified ssDNA gap; (c), the four-way junction at the reversed fork. Scale bar, 500 bp (=217 nm), 200 bp in inset. (b) Frequency of replication forks isolated from ESCs and differentiating ESCs (ESC-d) with the indicated number of ssDNA gaps. (d) Frequency of reversed replication forks isolated from ESC and ESC-d. The number of replication intermediates analysed is indicated in parentheses. Similar results were obtained in an independent experiment. (e) DNA fibre spreading of ESC, ESC-d and MEF. CldU/IdU-containing tracts were immunostained in red and green, respectively. Two representative fibres are shown for ESCs and ‘Differ. ESCs'. The IdU replicated track length was computed using Mann–Whitney test.