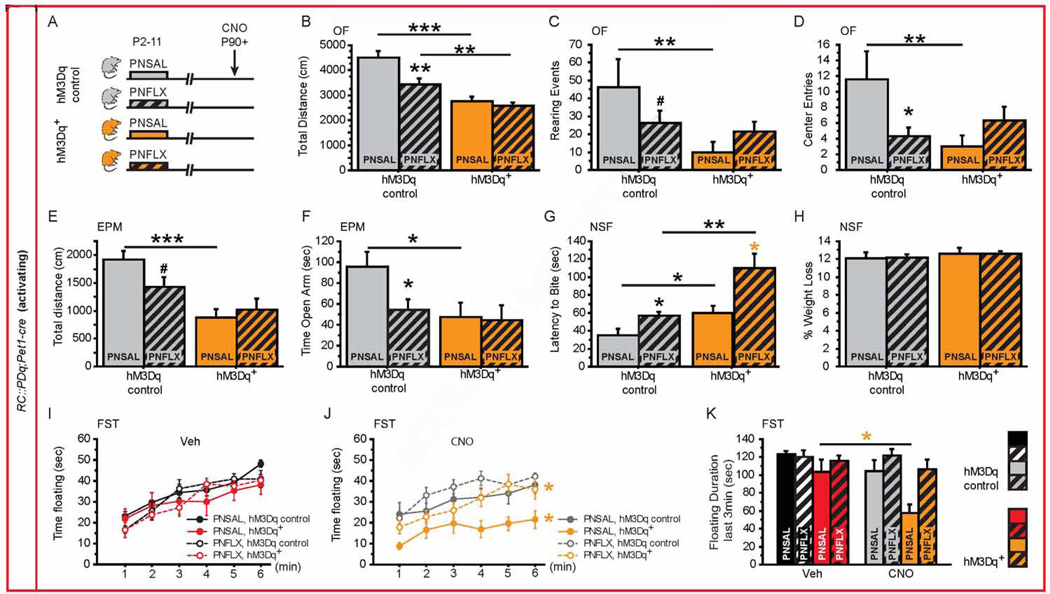
Figure 4. Behavioral consequences of increasing 5-HTergic neuronal activity in PNFLX mice.
(A) Schematic of experimental groups: hM3Dq+ mice (orange bars) and hM3Dq controls (grey bars) were injected with saline (PNSAL, plain bars) or FLX (PNFLX, dashed bars) from P2 to P11 and were submitted to behavioral tests upon CNO injections starting after P90.
(B–D) In the OF, PNSAL hM3Dq+ mice display decreased distance travelled (B), rearing events (C) and number of entries to the center (D) when compared to hM3Dq controls, while this response is blunted in PNFLX hM3Dq+ mice as compared with PNFLX hM3Dq controls. n = 7–11 per genotype and post-natal treatment.
(E–F) In the EPM, PNSAL hM3Dq+ mice display decreased distance travelled (E) and open arm time (F). n = 11–16 per genotype and post-natal treatment.
(G–H) Latency to bite the pellet in the NSF test is significantly increased in both PNSAL and PNFLX hM3Dq+ mice as compared with their controls (H). No change in the % weight loss was observed between PNSAL or PNFLX hM3Dq+ mice and their respective controls (H). n = 13–15 per genotype and post-natal treatment.
(I, J) In the FST, PNSAL and PNFLX hM3Dq+ mice spent less time floating during 6min of the test upon CNO (J) but not Veh (I) injections when compared to their respective hM3Dq controls. n = 13–16 per genotype and post-natal treatment.
(K) During the last 3 min of the FST, PNSAL hM3Dq+ mice float less after CNO exposure when compared to Veh treatment. n = 13–16 per genotype and post-natal treatment.
p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. EPM: elevated plus maze, NSF: novelty-suppressed feeding, OF: open field, FST: forced swim test.